Ethnopharmacological Profile, Phytochemistry and Therapeutic Potential of Aegle marmelos L. for the Treatment of Neurological Disorders
- PMID: 40535825
- PMCID: PMC12176473
- DOI: 10.1155/jnme/2275526
Ethnopharmacological Profile, Phytochemistry and Therapeutic Potential of Aegle marmelos L. for the Treatment of Neurological Disorders
Abstract
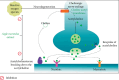
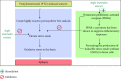
Aegle marmelos (L.) Corrêa, commonly known as the bael fruit tree, is a member of the Rutaceae family and holds significance in Ayurvedic herbal medicine due to its myriad therapeutic properties. This paper seeks to delve into the diverse benefits offered by the bael fruit tree, exploring various plant parts, including leaves, fruit, bark, and seeds, all of which contain bioactive compounds with therapeutic potential. The bael fruit, with its diverse phytochemical profile, exhibits potential health benefits ranging from radioprotection and antibacterial properties to antioxidant and hepatoprotective effects. Additionally, this review highlights the limited preclinical studies on AMs' efficacy in treating neurological disorders, emphasizing the need for more clinical trials to validate its potency and safety. Specifically, the effects and mechanisms of AM extract in addressing Alzheimer's disease, anxiety, depression, epilepsy and Parkinson's disease are explored. In conclusion, AM emerges as a plant of considerable nutritional and pharmacological value, with the potential to contribute significantly to the treatment of neurological disorders. Despite its promising attributes, the limited preclinical studies necessitate further clinical trials to confirm its efficacy. This review consolidates relevant studies, offering insights into AMs' ethnobotany, chemical constituents, pharmacological properties and potential application in neurological disorders. The comprehensive examination underscores the need for continued research to unlock the full therapeutic potential of this versatile plant.
Keywords: Aegle marmelos; Alzheimer's disease; Parkinson's disease; depression; epilepsy.
Copyright © 2025 Ashwani Sharma et al. Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Exploring pharmacological potential of Aegle marmelos: integrating traditional knowledge with modern physiology and molecular biology.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2025 Apr;31(4):521-543. doi: 10.1007/s12298-025-01586-2. Epub 2025 May 22. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2025. PMID: 40443470 Review.
-
Ethnobotanical Significance, Phytopharmacology, and Toxicological Profile of Limonia acidissima L. (Rutaceae): A Review.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025;28(9):1459-1490. doi: 10.2174/0113862073285538240417051928. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 38676498 Review.
-
Genetic diversity assessment of bael (Aegle marmelos) varieties using morphometric, yield, and quality traits under semi-arid conditions.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Aug 27;25(1):1143. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06985-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40866800 Free PMC article.
-
Genotypic diversity and nutritional profiling of Bael [Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa] genotypes in India.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 25;15(1):31231. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-12986-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40854911 Free PMC article.
-
Revealing the Curative Possibilities: A Comprehensive Exploration of Caffeic Acid.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025;26(9):1303-1313. doi: 10.2174/0113892010309341240517071344. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 38840396 Review.
References
-
- Who. Over 1 in 3 People Affected by Neurological Conditions, the Leading Cause of Illness and Disability Worldwide . World Health Organization; 2024.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

