Vitamin K: Metabolism, Genetic Influences, and Chronic Disease Outcomes
- PMID: 40535915
- PMCID: PMC12173841
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.70431
Vitamin K: Metabolism, Genetic Influences, and Chronic Disease Outcomes
Abstract
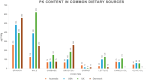
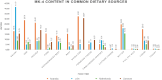
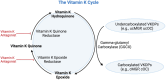
Vitamin K refers to a group of lipid-soluble vitamins that exist in two natural isoforms; phylloquinone (PK, vitamin K1) and menaquinones (MKs, vitamin K2). Phylloquinone, the primary dietary source, is found abundantly in green vegetables and plant oils. Menaquinones (MK-4 through MK-13) are synthesized by anaerobic bacteria and may be obtained through the diet from fermented foods and animal products (e.g., meats, dairy and eggs). Originally recognized for its role in blood coagulation, vitamin K is an essential cofactor for the posttranslational carboxylation of vitamin K-dependent proteins (VKDPs), which are implicated in various physiological processes including; blood coagulation, calcium homeostasis, as well as metabolic and inflammatory pathways. Therefore, vitamin K has attracted considerable research interest for its potential implications in several diseases. While promising, the specific roles of vitamin K in various health conditions, the quantity of vitamin K (both PK and MKs) required for the function of various VKDPs, and the influence of genetics on vitamin K metabolism, remain unclear. This review aims to (i) provide an overview of the structure, dietary sources, metabolism, and physiological roles of vitamin K, including those relating to; cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, respiratory conditions, musculoskeletal health and cancer; (ii) discuss the impact of genetic factors on vitamin K status and how such factors modulate the role of vitamin K in the aforementioned chronic diseases; and (iii) outline key directions for future research.
Keywords: bone health; cancer; cardiovascular disease; diabetes; vitamin K1; vitamin K2.
© 2025 The Author(s). Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The epigenetic potential of vitamin K2 in brain health.Epigenomics. 2025 Jul;17(10):681-690. doi: 10.1080/17501911.2025.2518916. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Epigenomics. 2025. PMID: 40506698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D: Production, Metabolism, and Mechanism of Action.2025 Jun 15. In: Feingold KR, Ahmed SF, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, Muzumdar R, Purnell J, Rey R, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. 2025 Jun 15. In: Feingold KR, Ahmed SF, Anawalt B, Blackman MR, Boyce A, Chrousos G, Corpas E, de Herder WW, Dhatariya K, Dungan K, Hofland J, Kalra S, Kaltsas G, Kapoor N, Koch C, Kopp P, Korbonits M, Kovacs CS, Kuohung W, Laferrère B, Levy M, McGee EA, McLachlan R, Muzumdar R, Purnell J, Rey R, Sahay R, Shah AS, Singer F, Sperling MA, Stratakis CA, Trence DL, Wilson DP, editors. Endotext [Internet]. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. PMID: 25905172 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular feature-based classification of retroperitoneal liposarcoma: a prospective cohort study.Elife. 2025 May 23;14:RP100887. doi: 10.7554/eLife.100887. Elife. 2025. PMID: 40407808 Free PMC article.
-
Defining disease severity in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis for the application to biomarker research: an interdisciplinary perspective.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jun 20;191(1):14-23. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae080. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38419411 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alfadda, A. , Masood A., Shaik S., Dekhil H., and Goran M.. 2013. “Association Between Osteocalcin, Metabolic Syndrome, and Cardiovascular Risk Factors: Role of Total and Undercarboxylated Osteocalcin in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes.” International Journal of Endocrinology 1: 197519. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Apalset, E. M. , Gjesdal C. G., Eide G. E., and Tell G. S.. 2011. “Intake of Vitamin K1 and K2 and Risk of Hip Fractures: The Hordaland Health Study.” Bone 49, no. 5: 990–995. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

