Fasting the mitochondria to prevent neurodegeneration: the role of ceramides
- PMID: 40535970
- PMCID: PMC12174400
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1602149
Fasting the mitochondria to prevent neurodegeneration: the role of ceramides
Abstract
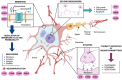
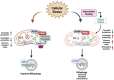
Neurodegenerative diseases affect up to 349.2 million individuals worldwide. Preclinical and clinical advances have documented that altered energy homeostasis and mitochondria dysfunction is a hallmark of neurological disorders. Diet-derived ceramides species might target and disrupt mitochondria function leading to defective energy balance and neurodegeneration. Ceramides as bioactive lipid species affect mitochondria function by several mechanism including changes in membrane chemical composition, inhibition of the respiratory chain, ROS overproduction and oxidative stress, and also by activating mitophagy. Promising avenues of intervention has documented that intermittent fasting (IF) is able to benefit and set proper energy metabolism. IF is an eating protocol that involves alternating periods of fasting with periods of eating which modulate ceramide metabolism and mitochondria function in neurons. This review will address the detrimental effect of ceramides on mitochondria membrane composition, respiratory chain, ROS dynamics and mitophagy in brain contributing to neurodegeneration. We will focus on effect of IF on ceramide metabolism as a potential avenue to improve mitochondria function and prevention of neurodegeneration.
Keywords: ceramides; intermittent fasting; microglia; mitophagy; neurodegeneration.
Copyright © 2025 Valenzuela-Ahumada, Mercado-Gómez, Viveros-Contreras, Guevara-Guzmán and Camacho-Morales.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

