Effects of Surya Namaskar yoga on perceived stress, anthropometric parameters, and physical fitness in overweight and obese female university students: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 40535981
- PMCID: PMC12171770
- DOI: 10.1142/S1013702525500027
Effects of Surya Namaskar yoga on perceived stress, anthropometric parameters, and physical fitness in overweight and obese female university students: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Stress and sedentary lifestyles negatively impact the physical fitness of overweight and obese female university students. Physical activity has been shown to promote psychological as well as physical wellness. However, the effects of Surya Namaskar (SN) yoga on stress and physical fitness remain unclear.
Objective: This study aimed to compare the physical fitness, anthropometric measures, and perceived stress between the SN yoga training program group and the control group.
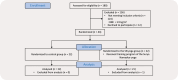
Methods: In a randomized controlled study, 44 overweight and obese female university students participated. For 8 weeks, the exercise group received training in SN yoga, whereas the control group was not permitted to participate in any form of exercise. At baseline and after 8 weeks of training, all participants completed the Thai Perceived Stress Scale-10 (T-PSS-10), and assessed the body mass index (BMI), waist-hip ratio, body fat percentage, maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max), and muscle strength and flexibility. We used the dependent t-test or Wilcoxon sign rank test to examine the differences between the T-PSS-10 and physical fitness within each group. The statistical differences of all parameters between the two groups were compared using an independent t-test or a Mann-Whitney U test. A p- was considered statistically significant.
Results: Compared to the baseline, the SN yoga group's post-training period had a significant increase ( ) in forward back flexibility, hand grip strength, leg strength, and VO2max, while a significant decrease ( ) in T-PSS-10 scores and BMI. In addition, we found a significant difference between the both groups in forward back flexibility and T-PSS-10 scores in the post-training period ( and , respectively).
Conclusion: This study's findings demonstrated that SN yoga is a useful exercise for enhancing overweight and obese female university students' perceived stress scales and physical fitness.
Keywords: Health promotion; mental health; physical activity; physical health; yoga.
© Hong Kong Physiotherapy Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest relevant to this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Victoire S, Ukwandu S, Ejuone O, Olunu EO. The influence of modern lifestyle on the health of medical students in a medical school in Dominica. J Adv Med Med Res 2022;34(10):57–64.
-
- Hailu GN, Gebru HB, Siyoum BD. Assessment of healthy diet and physical activity among students of Mekelle University, Northern Ethiopia: A cross-sectional study. Nutr Diet Suppl 2021;13:103–12.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
