A nomogram based on radiomic features from peri-prostatic adipose tissue for predicting bone metastasis in first-time diagnosed prostate cancer patients
- PMID: 40536175
- PMCID: PMC12184149
- DOI: 10.1080/21623945.2025.2517583
A nomogram based on radiomic features from peri-prostatic adipose tissue for predicting bone metastasis in first-time diagnosed prostate cancer patients
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate a radiomics-based nomogram using peri-prostatic adipose tissue (PPAT) features for predicting bone metastasis (BM) in newly diagnosed prostate cancer (PCa) patients.
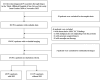
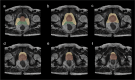
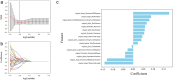
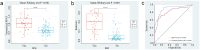
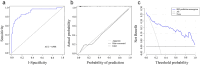
Methods: A retrospective study of 151 PCa patients (October 2010-November 2022) was conducted. Radiomic features were extracted from axial T2-weighted MRI of PPAT, and normalized PPAT was calculated as the ratio of PPAT volume to prostate volume. A radiomics score (Radscore) was developed using logistic regression with 16 features selected via LASSO regression. Independent predictors identified through univariate and multivariate logistic regression were used to construct a nomogram. Predictive performance was assessed using ROC curves, and internal validation involved 1000 bootstrapped iterations.
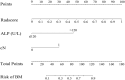
Results: The Radscore, based on 16 features, showed significant association with BM and outperformed normalized PPAT in predictive value. Independent predictors of BM included Radscore, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and clinical N stage (cN). A nomogram integrating these factors demonstrated strong discrimination (C-index: 0.908; 95% CI: 0.851-0.966) and calibration, with consistent results in validation (C-index: 0.903; 95% CI: 0.897-0.916). Decision curve analysis confirmed its clinical utility.
Conclusions: Radscore, cN, and ALP were identified as independent BM predictors. The developed nomogram enables accurate risk stratification and personalized BM predictions for newly diagnosed PCa patients.
Keywords: MRI; Prostate cancer; bone metastasis; peri-prostatic adipose tissue; radiomics.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiomics of Periprostatic Fat and Tumor Lesion Based on MRI Predicts the Pathological Upgrading of Prostate Cancer from Biopsy to Radical Prostatectomy.Acad Radiol. 2025 Aug;32(8):4607-4620. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2024.11.043. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Acad Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39730248
-
Development of a Radiomic-clinical Nomogram for Prediction of Survival in Patients with Nasal Extranodal Natural Killer/T-cell Lymphoma.Curr Med Imaging. 2025 Jun 19. doi: 10.2174/0115734056319914250605053257. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40551696
-
A nomogram based on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging radiomics for prediction of acute pancreatitis activity.BMC Med Imaging. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s12880-025-01778-y. BMC Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40597753 Free PMC article.
-
What Is the Negative Predictive Value of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Excluding Prostate Cancer at Biopsy? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis from the European Association of Urology Prostate Cancer Guidelines Panel.Eur Urol. 2017 Aug;72(2):250-266. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.02.026. Epub 2017 Mar 21. Eur Urol. 2017. PMID: 28336078
-
Diagnostic Performance of Magnetic Resonance Imaging for the Detection of Bone Metastasis in Prostate Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Eur Urol. 2018 Jan;73(1):81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.03.042. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 28412063
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
