A Tight-Knit Family: The Medium-Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductases of Monoterpene Indole Alkaloid Biosynthesis
- PMID: 40536199
- PMCID: PMC12224309
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5c00234
A Tight-Knit Family: The Medium-Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductases of Monoterpene Indole Alkaloid Biosynthesis
Abstract
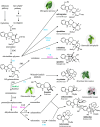
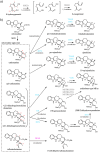
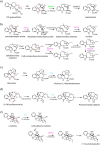
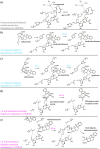
Medium-chain dehydrogenases/reductases (MDRs) are enzymes that are well-known for catalyzing the reversible reduction of ketones or aldehydes or oxidation of alcohols. However, the biosynthetic pathways of the monoterpene indole alkaloids (MIAs), an important class of natural products derived from plants, highlight that MDRs can also catalyze 1,2- and 1,4-α,β-unsaturated iminium reductions, as well as 1,4-α,β-unsaturated carbonyl reduction. The noncanonical activities of these MDRs correlate with distinct catalytic architectures centered on amino acid substitutions that impact catalytic zinc coordination, acid/base catalysis, and proton relay. These noncanonical MDR catalytic architectures likely arose within the MDR subfamily of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenases (CADs). This review summarizes the currently characterized MIA biosynthetic MDRs along with an analysis of the catalytic mechanisms, structural underpinnings, and phylogeny.
Keywords: alcohol dehydrogenase; carbonyl reduction; catalytic architecture; iminium reduction; medium-chain dehydrogenase/reductase; monoterpene indole alkaloid; noncanonical activity; plant natural products.
Figures



References
-
- Himes R. H., Kersey R. N., Heller-Bettinger I., Samson F. E.. Action of the Vinca Alkaloids Vincristine, Vinblastine, and Desacetyl Vinblastine Amide on Microtubules in Vitro. Cancer Res. 1976;36:3798–3802. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

