Scaffolding Protein ENH Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis and Growth Through Macrophage Recruitment and Polarization
- PMID: 40536254
- PMCID: PMC12442595
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202416476
Scaffolding Protein ENH Promotes Tumor Angiogenesis and Growth Through Macrophage Recruitment and Polarization
Abstract
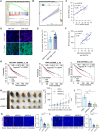
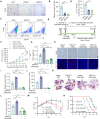
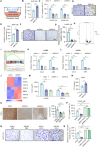
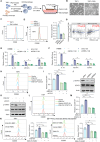
Angiogenesis is vital for tumor growth and metastasis, with tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) being key pro-angiogenic cells recruited by tumor-secreted chemokines. High levels of TAMs contribute to tumor progression and antiangiogenic therapy resistance. Therefore, intensive study of the regulatory mechanisms of TAMs recruitment during tumor development is important for the discovery of new antitumor and antiangiogenic therapeutic strategies. Here, we found that in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), ENH levels positively correlated with microvessel density and TAMs infiltration. Further exploration revealed that ENH promoted LUAD angiogenesis and growth by stimulating TAMs recruitment and M2 polarization. Mechanistically, ENH in LUAD induced YAP nuclear aggregation to promote CCL5 transcription, thereby increasing monocyte chemotaxis and ultimately increasing TAMs infiltration and M2 polarization. Besides, we found that ENH interacted with YAP through LIM domains, which significantly triggered the formation of YAP-KPNA2 complexes. Consequently, YAP is imported into the nucleus by KPNA2 and then promoted CCL5 transcription. Notably, ENH knockdown also significantly increased the chemosensitivity. Together, ENH functions in LUAD cells to mediate macrophage infiltration and M2 polarization, which in turn promotes tumor angiogenesis and growth, and targeting ENH offers a promising target for antiangiogenic therapy through immune modulation.
Keywords: ENH protein; YAP signaling; angiogenesis; lung adenocarcinoma; tumor‐associated macrophages.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Miller K. D., Nogueira L., Devasia T., Mariotto A. B., Yabroff K. R., Jemal A., Kramer J., Siegel R. L., CA. Cancer. J. Clin. 2022, 72, 409. - PubMed
-
- Zeng H., Chen W., Zheng R., Zhang S., Ji J. S., Zou X., Xia C., Sun K., Yang Z., Li H., Wang N., Han R., Liu S., Li H., Mu H., He Y., Xu Y., Fu Z., Zhou Y., Jiang J., Yang Y., Chen J., Wei K., Fan D., Wang J., Fu F., Zhao D., Song G., Chen J., Jiang C., et al., Lancet Glob. Health 2018, 6, 555.
-
- Weis S. M., Cheresh D. A., Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1359. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
