Understanding the pro- & anti-inflammatory cytokine profile in Japanese encephalitis & their implications in survival outcome
- PMID: 40536377
- PMCID: PMC12178199
- DOI: 10.25259/IJMR_1410_2024
Understanding the pro- & anti-inflammatory cytokine profile in Japanese encephalitis & their implications in survival outcome
Abstract
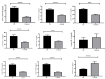
Background & objectives We aimed to conduct a comprehensive analysis of the cytokine profile in Japanese encephalitis (JE) patients and healthy individuals. Additionally, the correlation between the cytokines and the disease outcome in terms of survival or non-survival was also studied. Methods The study included 72 laboratory-confirmed JE cases and 50 healthy controls. Plasma levels of cytokines viz., GM-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-12, IL-13, and TNF-α were analysed using Bio-plex200 (Bio-Rad) following manufacturer's guidelines and compared between JE patients and healthy control group. Additionally, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) was done for the quantification of expression of the above-mentioned cytokine genes. Results Except IL-4 and IL-13, the levels of GM-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-2, IL-5, IL-10, IL-12, and TNF-α were significantly higher in JE patients in comparison to healthy controls. Significantly upregulated expression of IL-12, IL-10, and TNF-α was observed in the JE group as compared to that in healthy controls. Additionally, significantly downregulated expression of IL-4and IL-13 was observed in the JE group compared to the control group. Interpretation & conclusions A higher level of several pro-inflammatory cytokines and downregulation of a few anti-inflammatory cytokines were observed in JE patients compared to the healthy controls indicating co-association of inflammation with disease severity. Hence, a regulator of these pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines may stand out as a potential candidate for therapy in JE.
Keywords: Blood brain barrier; IL; Japanese encephalitis; TNF-α; cytokine; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of cytokines and vitamin D in benign and malignant thyroid diseases.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23493. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-06882-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40604072 Free PMC article.
-
A reduction in serum IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, and GM-CSF serves as potential markers for a positive outcome to lumbar epidural steroid injections.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 22;20(8):e0329552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0329552. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40844981 Free PMC article.
-
[Experimental study of anti-tumor immunologic response functions after combined treatment of cryoablation with GM-CSF for colorectal cancer liver metastases].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2025 Jul 1;64(7):670-674. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20241115-00757. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40605293 Chinese.
-
Mitigation and Management of Common Toxicities Associated with the Administration of CAR-T Therapies in Oncology Patients.Drug Saf. 2025 Jul;48(7):719-737. doi: 10.1007/s40264-025-01538-5. Epub 2025 Mar 19. Drug Saf. 2025. PMID: 40108072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological and electronic cigarette interventions for smoking cessation in adults: component network meta-analyses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Sep 12;9(9):CD015226. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015226.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37696529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fischer M, Hills S, Staples E, Johnson B, Yaich M, Solomon T. Japanese encephalitis prevention and control: advances, challenges, and new initiatives. Emerging Infections. 2008;8:93–124.
-
- Chen CJ, Ou YC, Lin SY, Raung SL, Liao SL, Lai CY, et al. Glial activation involvement in neuronal death by Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J Gen Virol. 2010;91:1028–37. - PubMed
-
- Das S, Mishra MK, Ghosh J, Basu A. Japanese encephalitis virus infection induces IL-18 and IL-1beta in microglia and astrocytes: Correlation with in vitro cytokine responsiveness of glial cells and subsequent neuronal death. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;195:60–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

