KAT6A and KAT7 Histone Acetyltransferase Complexes Are Molecular Dependencies and Therapeutic Targets in NUP98-Rearranged Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 40536430
- PMCID: PMC12498098
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-1772
KAT6A and KAT7 Histone Acetyltransferase Complexes Are Molecular Dependencies and Therapeutic Targets in NUP98-Rearranged Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
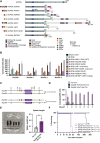
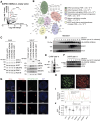
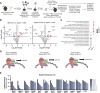
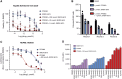
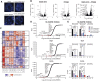
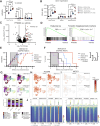
NUP98 fusion oncoproteins (FO) are a hallmark of childhood acute myeloid leukemia. NUP98 FOs drive leukemogenesis through phase-separated condensate formation and maintenance of an active chromatin landscape at stem cell-associated genes in cooperation with epigenetic regulators. In this study, we show that MYST family histone acetyltransferase (HAT) complex proteins, including KAT6A/MOZ, KAT7/HBO1, and the common KAT6A/7 complex subunit BRPF1, associate with NUP98 FOs on chromatin and within condensates. MYST HATs are molecular dependencies in NUP98-rearranged (NUP98-r) leukemia, and genetic inactivation or pharmacologic inhibition of KAT6A and KAT7 impairs NUP98-r cell fitness. KAT6A/7 inhibition decreased global H3K23ac levels, displaced NUP98::HOXA9 from chromatin at the Meis1 locus, and led to myeloid cell differentiation. Additionally, KAT6A/7 inhibition decreased leukemic burden in multiple NUP98-r leukemia xenograft mouse models, synergized with menin inhibitor treatment, and was efficacious in menin inhibitor-resistant cells. In summary, we show that MYST family HATs are therapeutically actionable dependencies in NUP98-r acute myeloid leukemia.
Significance: KAT6A and KAT7 associate with NUP98 FOs to drive leukemogenesis. Inhibition of their HAT activity is an effective therapeutic strategy in NUP98-r leukemias, including those resistant to menin inhibition. Moreover, combined KAT6A/7 and menin inhibition is synergistic, supporting clinical translation to improve outcomes for NUP98 FO-driven leukemias.
©2025 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
N.L. Michmerhuizen reports grants from the NCI during the conduct of the study. E.B. Heikamp reports grants from the NCI, the American Society of Hematology, the Charles H. Hood Foundation, the Children’s Cancer Research Fund, the Hyundai Hope on Wheels Foundation, and the Rose Family Fellowship during the conduct of the study. I. Iacobucci reports other support from Arima Genomics, Mission Bio, and Takara outside the submitted work. M. Umeda reports personal fees from AstraZeneca outside the submitted work. V. Subramanyam reports grants from the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute during the conduct of the study. D.V. Wenge reports grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft during the conduct of the study. S.B. Pounds reports grants from the US NIH during the conduct of the study. A. Kentsis reports that he is a consultant for Novartis, Rgenta, Blueprint, Syndax, and Sellas. H. Chi reports grants from the NIH during the conduct of the study as well as other support from Kumquat Biosciences and TCura Bioscience outside the submitted work and that he has a patent for patents/patent applications in the field of immunotherapy pending. J.M. Klco reports grants from the NCI during the conduct of the study. S.A. Armstrong reports personal fees from C4 Therapeutics, Neomorph, Stelexis Therapeutics, Hyku Biosciences, AstraZeneca, and Accent Therapeutics outside the submitted work and that he has a patent for menin inhibition (WO/2017/132398A1) issued and licensed. C.G. Mullighan reports personal fees from Illumina during the conduct of the study as well as grants from Pfizer and AbbVie outside the submitted work. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Figures

References
-
- Hollink IH, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM, Arentsen-Peters STCJM, Pratcorona M, Abbas S, Kuipers JE, et al. NUP98/NSD1 characterizes a novel poor prognostic group in acute myeloid leukemia with a distinct HOX gene expression pattern. Blood 2011;118:3645–56. - PubMed
-
- de Rooij JDE, Hollink IHIM, Arentsen-Peters STCJM, van Galen JF, Berna Beverloo H, Baruchel A, et al. NUP98/JARID1A is a novel recurrent abnormality in pediatric acute megakaryoblastic leukemia with a distinct HOX gene expression pattern. Leukemia 2013;27:2280–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA279891-01A1/Center for Cancer Research (CCR)
- T32 CA236738/Center for Cancer Research (CCR)
- R01 CA204396/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA236748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA243124/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA066996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA279891/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA021765/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- American Society of Hematology (ASH)
- Burroughs Wellcome Fund (BWF)
- R01 CA246125/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA253188/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 CA283256/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA259273/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197695/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Hyundai Hope On Wheels (Hope On Wheels)
- Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (LLS)
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Charles H. Hood Foundation (CHF)
- F32 CA261011/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- St. Jude Children's Research Hospital
- P30 CA006516/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA06516/Center for Cancer Research (CCR)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

