Pathogenicity and Virulence of Coxiella burnetii: Focus on Q fever
- PMID: 40536474
- PMCID: PMC12184199
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2495842
Pathogenicity and Virulence of Coxiella burnetii: Focus on Q fever
Abstract
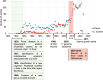
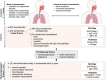
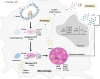
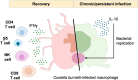
Coxiella burnetii is responsible for Q fever, a zoonosis that mainly manifests as a mild acute infection and may persist in specific individuals causing severe complications, including endocarditis and vascular infections. Transmission mainly occurs through the inhalation of aerosols, underlining bacterial resistance to environmental stress. C. burnetii is an intracellular gram-negative pathogen that can infect and survive in monocytes and macrophages and replicate within acidic compartments. C. burnetii expresses several virulence factors, including lipopolysaccharide and a type IV secretion system, which are involved in hijacking several functions of the immune system and controlling cell death. This review summarizes research on C. burnetii infection from clinical presentation of Q fever to bacterial and host factors of virulence. It compiles immunological data associated with bacterial cure or persistence and discusses a potential link between C. burnetii-macrophage interaction and immune dysregulation of Q fever.
Keywords: Coxiella burnetii; Q fever; macrophages; virulence factors.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Davis GE, Cox HR, Parker RR, et al. A filter-passing infectious agent isolated from ticks. Public Health Rep (1896–1970). 1938;53:2259.
-
- Cox HR. Rickettsia Diaporica and American Q fever 1. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1940;s1–20(4):463–469. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1940.s1-20.463 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources