Degradation of beechwood xylan using food-grade bacteria-like particles displaying β-xylosidase from Limosilactobacillus fermentum
- PMID: 40536589
- PMCID: PMC12179037
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-025-00898-1
Degradation of beechwood xylan using food-grade bacteria-like particles displaying β-xylosidase from Limosilactobacillus fermentum
Abstract
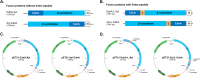
The display of enzymes on bacterial surfaces is an interesting approach for immobilising industrially important biocatalysts. In recent years, non-recombinant surface display using food-grade bacteria, such as lactic acid bacteria (LAB), have gained interest because of their safety, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. β-Xylosidase is one of the many biocatalytic enzymes targeted for immobilisation due to its key role in the complete saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass, including xylan hemicellulose. Recently, the xylose-tolerant β-xylosidase, LfXyl43, was identified in Limosilactobacillus fermentum. LfXyl43 is capable of producing xylose from the degradation of xylo-oligosaccharides (XOS) and beechwood xylan. This study aimed to immobilise this new biocatalyst on the surface of LAB-derived bacteria-like particles (BLP) and investigate its applicability and reusability in the degradation of xylan hemicellulose. Additionally, the influence of the anchor position and the presence of linker peptides on the display and activity of the β-xylosidase was investigated. Four expression vectors were constructed to express different anchor-xylosidase fusion proteins. Upon expression and purification, all anchor-xylosidase fusion proteins were active towards the artificial substrate p-nitrophenyl-β-D-xylopyranoside. In addition, all anchor-xylosidase fusion proteins were successfully displayed on the surface of BLP. However, only the β-xylosidases with linker peptide showed hydrolytic activity after immobilisation on BLP. BLP displaying β-xylosidases demonstrated high activity against XOS and beechwood xylan, thereby producing high amounts of xylose. Moreover, the immobilised enzyme demonstrated reusability across several bioconversion cycles. Overall, this study highlights the potential industrial application of surface-displayed β-xylosidase for the effective degradation of lignocellulosic biomass.
Keywords: Beta-xylosidase; Biocatalyst; Immobilisation; Lactic acid bacteria; Surface display; Xylan.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Heterologous expression and characterization of xylose-tolerant GH 43 family β-xylosidase/α-L-arabinofuranosidase from Limosilactobacillus fermentum and its application in xylan degradation.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 10;13:1564764. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1564764. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40129454 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying promoters to enhance heterologous gene expression in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains cultivated on non-native substrates.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Jul 26;109(1):173. doi: 10.1007/s00253-025-13563-6. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40715790 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing flagellin of Ligilactobacillus agilis as a surface display scaffold for an HIV-1 epitope.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025 Jun 18;91(6):e0067425. doi: 10.1128/aem.00674-25. Epub 2025 May 29. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40439423 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological and electronic cigarette interventions for smoking cessation in adults: component network meta-analyses.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Sep 12;9(9):CD015226. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015226.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37696529 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ali A, Abdulameer MK, Mahdi MH et al (2024) Utilizing a Deformation/Aggregation-Based approach for determination of selenium using plasmonic silver nanoparticles. Plasmonics 20:2797–2805. 10.1007/s11468-024-02481-4
-
- Arai R, Ueda H, Kitayama A et al (2001) Design of the linkers which effectively separate domains of a bifunctional fusion protein. Protein Eng Des Sel 14:529–532. 10.1093/protein/14.8.529 - PubMed
-
- Bosetto A, Justo PI, Zanardi B et al (2016) Research progress concerning fungal and bacterial β-Xylosidases. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 178:766–795. 10.1007/s12010-015-1908-4 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

