Hip denervation: an approach for relieving pain, restoring function, and reducing inflammation in juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients
- PMID: 40536645
- PMCID: PMC12289715
- DOI: 10.1007/s10067-025-07490-0
Hip denervation: an approach for relieving pain, restoring function, and reducing inflammation in juvenile idiopathic arthritis patients
Abstract
Background: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) frequently involves the hip joint, leading to significant pain, functional impairment, and long-term joint damage. Conventional treatment strategies, including pharmacologic therapy and intra-articular injections, may not provide adequate control. Hip denervation (HD) has emerged as a potential interventional approach for pain management in various musculoskeletal conditions, but its role in JIA-associated hip arthritis remains unclear. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of HD in JIA patients with unilateral hip arthritis on pain, function, and inflammatory parameters.
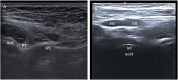
Methods: One hundred twenty JIA patients were diagnosed according to the ILAR criteria with unilateral hip arthritis. They were assigned randomly into three groups: group 1 received hip denervation, group 2 received subcutaneous saline, and group 3 received intra-articular triamcinolone. Visual analog scale (VAS), sonography of large joints in rheumatology (SOLAR) score, tenderness, and Harris Hip score (HHS) were assessed at 0-, 2-, and 16-week intervals. Tenderness was evaluated by a semi-quantitative score at the same intervals. Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score (JADAS) was assessed at baseline.
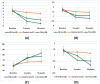
Results: Over the 16-week study period, HD delivered remarkable outcomes, with VAS dropping from 5.48 ± 2.04 at baseline to 0.83 ± 0.50 (p < 0.0001), tenderness scores decreasing from 1.80 ± 0.82 to 0.80 ± 0.41 (p < 0.0001), and SOLAR score significantly reduced from 1.38 ± 0.59 to 0.15 ± 0.06 (p < 0.0001). Functional recovery was equally impressive, as HHS soared from 59.60 ± 9.89 to 83.27 ± 6.42 (p < 0.0001), surpassing outcomes seen with intra-articular steroids and placebo. Favorable responses were strongly associated with shorter disease duration, higher baseline VAS and SOLAR scores, and the oligoarticular subtype, while RF positivity predicted diminished improvement.
Conclusion: Hip denervation showed promising results in regaining functions, alleviating pain, tenderness, and inflammation of the hip joint in JIA patients. Key Points • This study is the first to evaluate HD in JIA, showing its potential to alleviate pain, improve function, and reduce inflammation. • HD demonstrated sustained benefits at 16 weeks, surpassing intra-articular steroids in controlling symptoms and modifying the inflammatory cascade. • It offers a minimally invasive, effective alternative for JIA-related hip arthritis, addressing the limitations of conventional therapies.
Keywords: Hip denervation; Juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethical standards. Disclosures: None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Methotrexate for juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Feb 9;2(2):CD003129. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003129.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38334147 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors for juvenile idiopathic arthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Feb 20;2(2):CD013715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39976227
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of strategies for reducing fracture risk in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis with additional data on long-term risk of fracture and cost of disease management.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Mar;12(3):iii-ix, xi-xiv, 1-208. doi: 10.3310/hta12030. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18284894
-
Summary of AHRQ's Comparative Effectiveness Review of Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs for Children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis.J Manag Care Pharm. 2012 Jan-Feb;18(1 Suppl B):1-16. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2012.18.S1-B.1. J Manag Care Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22376227 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise for hand osteoarthritis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 31;1(1):CD010388. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010388.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28141914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bouden S, Chekaya NB, Tekaya AB, Saidane O, Tekaya R, Mahmoud I et al (2021) AB0730 Hip involvement in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. BMJ Publishing Group Ltd
-
- Singh JA, Cleveland JD (2021) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis is associated with higher healthcare utilization after total knee or hip replacement. Scand J Rheumatol 50(1):34–39 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

