The application of telmisartan in central nervous system disorders
- PMID: 40536710
- PMCID: PMC12443940
- DOI: 10.1007/s43440-025-00737-2
The application of telmisartan in central nervous system disorders
Abstract
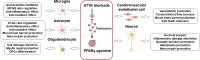
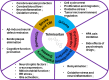
Telmisartan, a well-established antihypertensive drug, has shown promising therapeutic potential for a variety of central nervous system (CNS) disorders. This review outlines the fundamental characteristics of telmisartan, focusing on its dual pharmacological effects as an angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) antagonist and a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) γ activator. These mechanisms underpin its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects, which are essential to its therapeutic benefits in CNS diseases. Telmisartan modulates key cellular components of the CNS, including microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, vascular endothelial cells, and neurons, thereby offering protection against neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, and neuronal damage. We summarize telmisartan's efficacy in addressing a range of neurological conditions, such as stroke, traumatic brain injury, dementia, Parkinson's disease, demyelinating diseases, psychiatric disorders, and gliomas. By targeting multiple pathways involved in these disorders, telmisartan demonstrates potential as both an adjunctive and standalone therapy. Its ability to attenuate neuroinflammation and promote cellular repair highlights its versatility in CNS disease management. This review underscores the potential of telmisartan as a valuable therapeutic option for CNS disorders, warranting continued exploration to optimize its clinical application.
Keywords: AT1R; Central nervous system; Neuroinflammation; PPARγ; Telmisartan.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Michel MC, Foster C, Brunner HR, Liu L.A systematic comparison of the properties of clinically used angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists. Pharmacol Rev. 2013;65(2):809–48. - PubMed
-
- Destro M, Cagnoni F, Dognini GP, Galimberti V, Taietti C, Cavalleri C, et al. Telmisartan: just an antihypertensive agent? A literature review. Expert Opin Pharmacother 2011;12:2719–35. - PubMed
-
- Hattori N, Yamada A, Nakatsuji S, Matsuda T, Nishiyama N, Shimatsu A.Telmisartan is the most effective ARB to increase adiponectin via PPARα in adipocytes. J Mol Endocrinol. 2022;69(1):259–68. - PubMed
-
- Deppe S, Böger RH, Weiss J, Benndorf RA.Telmisartan: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2010;6(7):863–71. - PubMed
-
- Fu XX, Wei B, Cao HM, Duan R, Deng Y, Lian HW, et al. Telmisartan Alleviates Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Neuropathologies and Cognitive Impairments. J Alzheimers Dis 2023;94:919–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
