Cross-species efficacy of AAV-mediated ARSA replacement for metachromatic leukodystrophy
- PMID: 40536808
- PMCID: PMC12352910
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI185001
Cross-species efficacy of AAV-mediated ARSA replacement for metachromatic leukodystrophy
Abstract
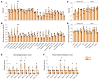
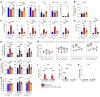
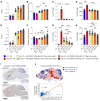
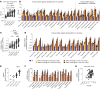
Metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD) is an autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder caused by mutations in the arylsulfatase A (ARSA) gene, resulting in lower sulfatase activity and the toxic accumulation of sulfatides in the central and peripheral nervous system. Children account for 70% of cases and become progressively disabled, with death occurring within 10 years of disease onset. Gene therapy approaches to restore ARSA expression via adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors have been promising but hampered by limited brain biodistribution. We report the development of an engineered capsid, AAV.GMU01, demonstrating superior biodistribution and transgene expression in the central nervous system of nonhuman primates (NHPs). Next, we show that AAV.GMU01-ARSA-treated MLD mice exhibit persistent, normal levels of sulfatase activity and a concomitant reduction in toxic sulfatides. Treated mice also show a reduction in MLD-associated pathology and auditory dysfunction. Lastly, we demonstrate that treatment with AAV.GMU01-ARSA in NHPs is well tolerated and results in potentially therapeutic ARSA expression in the brain. In summary, we propose AAV.GMU01-ARSA-mediated gene replacement as a clinically viable approach to achieve broad and therapeutic levels of ARSA.
Keywords: Gene therapy; Genetic diseases; Genetics; Neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


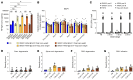
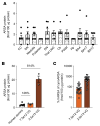
References
-
- Gieselmann V, Ingeborg KM. Metachromatic leukodystrophy. In: Valle DL, et al. eds. The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill; 2019: Chapter 179.
-
- Aubourg P. Gene therapy for leukodystrophy: progress, challenges and opportunities. Expert Opin Orphan Drugs. 2016;4(4):359–367. doi: 10.1517/21678707.2016.1151352. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

