Cortical Cerebral Microinfarcts in Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage on 3T and 7T MRI
- PMID: 40537072
- PMCID: PMC12187387
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000213642
Cortical Cerebral Microinfarcts in Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage on 3T and 7T MRI
Abstract
Background and objectives: MRI markers of cerebral small vessel disease (cSVD) in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (sICH) have provided insight in the underlying vascular pathology. Cortical cerebral microinfarcts (CMIs) are a relatively novel marker of cSVD. We aimed to assess presence and location within the cortex of CMIs in patients with sICH on 3T and 7T MRI, and to determine their association with hematoma location and other neuroimaging markers of cSVD.
Methods: From a multicenter prospective observational cohort study, we included consecutive adult patients who underwent 3T and/or 7T MRI within 3 months after sICH. We determined presence and location of CMIs within the cortex (superficial or deeper layers; on 7T MRI) and assessed associations between presence of cortical CMIs and vascular risk factors, hematoma location, and other MRI markers of cSVD with multiple regression analyses.
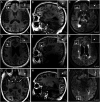
Results: We included 135 patients (mean age 63 years; 30% female). On 3T MRIs, we found 100 cortical CMIs in 57 patients (42%, median number 2, interquartile range [IQR] 1-3; lobar ICH 24 of 58 patients [41%]; non-lobar ICH 33 of 77 patients [43%]). On 7T MRI images, we found 59 cortical CMIs in 28 of 40 patients (70%; median number of 2, IQR 1-3; lobar ICH 8 of 12 patients [67%]; non-lobar ICH 20 of 28 patients [71%]). Presence of cortical CMIs was associated with history of TIA/ischemic stroke (relative risk [RR] 2.7, 95% CI 1.1-6.4), but not with other vascular risk factors or any of the MRI markers of cSVD. On 7T MRI, CMIs were located in the superficial part of the cortex in 30% of patients with lobar vs 5% of patients with non-lobar ICH (RR 2.7, 95% CI 1.5-5.0).
Discussion: Cortical CMIs are a common finding in patients with sICH on both 3T and 7T MRIs with a similar frequency in patients with lobar and non-lobar sICH. Patients with lobar sICH, more often have CMIs in the superficial part of the cortex than those with non-lobar sICH. Location of CMIs within the cortex might provide insight into the underlying type of small vessel disease in sICH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no disclosures relevant to the manuscript. Go to
Figures
References
-
- Rodrigues MA, Samarasekera N, Lerpiniere C, et al. The Edinburgh CT and genetic diagnostic criteria for lobar intracerebral haemorrhage associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy: model development and diagnostic test accuracy study. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17(3):232-240. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30006-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
