Positive Effect of Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Consumption on Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women Assessed by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry-Based 3-Dimensional Modeling
- PMID: 40537107
- PMCID: PMC12183358
- DOI: 10.11005/jbm.24.827
Positive Effect of Yerba Mate (Ilex paraguariensis) Consumption on Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women Assessed by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry-Based 3-Dimensional Modeling
Abstract
Background: Yerba mate (YM) drinking is associated with higher lumbar spine and femoral neck bone mineral density (BMD) in postmenopausal women. We analyzed its effect on total hip BMD and reported the contribution of the trabecular and cortical components to this effect.
Methods: A control group of 147 non-drinkers was compared to 153 YM drinkers. Left hip BMD was measured using dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), and three-dimensional (3D)-Shaper software was used to estimate integral volumetric BMD (vBMD), cortical surface BMD (sBMD), and trabecular vBMD through 3D modeling.
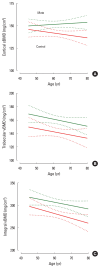
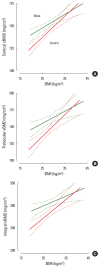
Results: No significant difference was found between groups in either age (p=0.746) or body mass index (BMI; p=0.329). The YM group had significantly higher total hip BMD, integral vBMD, cortical sBMD, and trabecular BMD (all p<0.0001). The frequency of DXA-based osteoporosis diagnosis was lower in YM drinkers (3.3% vs. 10.9%; odds ratio [OR], 0.276). The rate of low-impact fractures was significantly reduced in YM drinkers (5.9% vs. 12.9%; OR, 2.197). Linear regression analyses revealed that cortical and trabecular parameters correlated positively with BMI and negatively with age in both groups. The slope of the lines did not differ between groups, but the elevation was uniformly higher in the YM group (p=0.0004 to p<0.0001).
Conclusions: Our study provides novel insights into YM consumption and bone health in postmenopausal women. We confirm its positive association with BMD and demonstrate, for the first time, that both cortical and trabecular compartments contribute to this effect. Our findings also suggest a potential protective role of YM against osteoporosis and fragility fractures.
Keywords: Bone and bones; Bone density; Ilex paraguariensis; Osteoporosis; Postmenopause.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
3D-DXA reveals significant effects of burosumab on trabecular and cortical skeletal envelopes in symptomatic adults with X-linked Hypophosphatemia.J Bone Miner Res. 2025 Jul 13:zjaf092. doi: 10.1093/jbmr/zjaf092. Online ahead of print. J Bone Miner Res. 2025. PMID: 40652299
-
HR-pQCT reveals marked trabecular and cortical structural deficits in women with pregnancy and lactation-associated osteoporosis (PLO).J Bone Miner Res. 2024 Dec 31;40(1):38-49. doi: 10.1093/jbmr/zjae167. J Bone Miner Res. 2024. PMID: 39423251
-
Bone evaluation and relationship between body composition and bone mass in anorexia nervosa followed up by a multidisciplinary team.Endocrine. 2025 Jul;89(1):259-266. doi: 10.1007/s12020-025-04231-w. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Endocrine. 2025. PMID: 40249501
-
Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article.
-
Risedronate for the primary and secondary prevention of osteoporotic fractures in postmenopausal women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 3;5(5):CD004523. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004523.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35502787 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

