Multi-ancestry genome-wide association analyses incorporating SNP-by-psychosocial interactions identify novel loci for serum lipids
- PMID: 40537477
- PMCID: PMC12179276
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-025-03418-z
Multi-ancestry genome-wide association analyses incorporating SNP-by-psychosocial interactions identify novel loci for serum lipids
Abstract
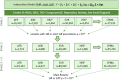
Serum lipid levels, which are influenced by both genetic and environmental factors, are key determinants of cardiometabolic health and are influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Improving our understanding of their underlying biological mechanisms can have important public health and therapeutic implications. Although psychosocial factors, including depression, anxiety, and perceived social support, are associated with serum lipid levels, it is unknown if they modify the effect of genetic loci that influence lipids. We conducted a genome-wide gene-by-psychosocial factor interaction (G×Psy) study in up to 133,157 individuals to evaluate if G×Psy influences serum lipid levels. We conducted a two-stage meta-analysis of G×Psy using both a one-degree of freedom (1df) interaction test and a joint 2df test of the main and interaction effects. In Stage 1, we performed G×Psy analyses on up to 77,413 individuals and promising associations (P < 10-5) were evaluated in up to 55,744 independent samples in Stage 2. Significant findings (P < 5 × 10-8) were identified based on meta-analyses of the two stages. There were 10,230 variants from 120 loci significantly associated with serum lipids. We identified novel associations for variants in four loci using the 1df test of interaction, and five additional loci using the 2df joint test that were independent of known lipid loci. Of these 9 loci, 7 could not have been detected without modeling the interaction as there was no evidence of association in a standard GWAS model. The genetic diversity of included samples was key in identifying these novel loci: four of the lead variants displayed very low frequency in European ancestry populations. Functional annotation highlighted promising loci for further experimental follow-up, particularly rs73597733 (MACROD2), rs59808825 (GRAMD1B), and rs11702544 (RRP1B). Notably, one of the genes in identified loci (RRP1B) was found to be a target of the approved drug Atenolol suggesting potential for drug repurposing. Overall, our findings suggest that taking interaction between genetic variants and psychosocial factors into account and including genetically diverse populations can lead to novel discoveries for serum lipids.
© 2025. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare the following competing interests: BMP serves on the Data and Safety Monitoring Board of a clinical trial funded by the manufacturer (Zoll LifeCor) and on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Access Project funded by Johnson & Johnson; CMvD was sponsored by GlaxoSmithKline; HJG received travel grants and speakers honoraria from Fresenius Medical Care, Neuraxpharm and Janssen Cilag as well as research funding from Fresenius Medical Care; JBJ serves in the Advisory Board Novartis; Patent holder with Biocompatibles UK Ltd. (Franham, Surrey, UK) (Title: Treatment of eye diseases using encapsulated cells encoding and secreting neuroprotective factor and / or anti-angiogenic factor; Patent number: 20120263794), and Europäische Patentanmeldung 16 720 043.5 and Patent application US 2019 0085065 A1 (Agents for use in the therapeutic or prophylactic treatment of myopia or hyperopia). Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate: For all participating cohorts, the appropriate institutional review boards approved research activities and informed consent was obtained from each participant. Further details on all participating cohorts is given in the Supplementary Note.
Figures

References
-
- Psaty BM, O’Donnell CJ, Gudnason V, Lunetta KL, Folsom AR, Rotter JI, et al. Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology (CHARGE) Consortium: design of prospective meta-analyses of genome-wide association studies from 5 cohorts. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2009;2:73–80. 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.108.829747. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rao DC, Sung YJ, Winkler TW, Schwander K, Borecki I, Cupples LA, et al. Multiancestry study of gene-lifestyle interactions for cardiovascular traits in 610 475 individuals from 124 cohorts: design and rationale. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2017;10:e001649 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.116.001649. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

