Sea dragon metabolome and lipidome unveil bioactive functional food candidates with sepsis therapeutic activities
- PMID: 40537493
- PMCID: PMC12179263
- DOI: 10.1038/s41538-025-00469-w
Sea dragon metabolome and lipidome unveil bioactive functional food candidates with sepsis therapeutic activities
Abstract
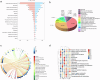
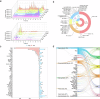
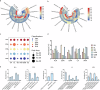
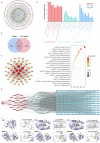
Sea dragons (Syngnathus) are valuable marine resources with notable interspecific phenotypic similarities and variations in composition and efficacy. This study employed multi-omics technologies to comprehensively analyze and structurally identify the molecular components of six species of Syngnathus, effectively screening interspecific differential markers. Untargeted metabolomics revealed a total of 18 classes and 2264 metabolites, and lipids were found to be the principal differential metabolites. Lipidomics were utilized for in-depth lipid detection, expanding the original 412 lipids detected through metabolomics to 2078 lipids, among which 47 differential metabolites and 138 differential lipids were selected from multi-omics results. The integration of network pharmacology and molecular docking elucidated the multifactorial mechanisms by which Syngnathus exerts anti-sepsis effects, including modulation of inflammatory responses, and regulation of apoptosis, while identifying key targets such as IL6, STAT3, and MAPK14. This study suggests that they may have potential as natural sources for the development of anti-sepsis foods. Further studies on their bioavailability and in vitro and in vivo efficacy are required in the future.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Understanding mechanisms of Polygonatum sibiricum-derived exosome-like nanoparticles against breast cancer through an integrated metabolomics and network pharmacology analysis.Front Chem. 2025 Jun 6;13:1559758. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2025.1559758. eCollection 2025. Front Chem. 2025. PMID: 40547857 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
References
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. In Beijing: China Medical Science Press. 1, 276 (2010).
-
- Chen, L., Wang, X. & Huang, B. The genus Hippocampus—a review on traditional medicinal uses, chemical constituents and pharmacological properties. J. Ethnopharmacol.162, 104–111 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Zhang, D. M. et al. Nano-LC-ESI MS/MS analysis of proteins in dried sea dragon Solenognathus hardwickii and bioinformatic analysis of its protein expression profiling. Chin. J. Nat. Med.14, 709–713 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Ng, T. B. & Lam, Y. W. Solenin, a novel protein with translation-inhibiting activity from the traditional Chinese medicinal fish, the sea dragon Solenognathus hardwickii. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol.34, 625–631 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Jiang, Z. et al. Insight into the binding of ACE-inhibitory peptides to angiotensin-converting enzyme: a molecular simulation. Mol. Simula.45, 215–222 (2019).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

