Baseline levels and dynamic changes of cfDNA, tumor fraction and mutations to anticipate the clinical course of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients treated with first-line atezolizumab and chemotherapy: an hypothesis generating study (CATS/ML43257)
- PMID: 40537796
- PMCID: PMC12178010
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-025-03434-3
Baseline levels and dynamic changes of cfDNA, tumor fraction and mutations to anticipate the clinical course of small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients treated with first-line atezolizumab and chemotherapy: an hypothesis generating study (CATS/ML43257)
Abstract
Background: Atezolizumab (A) plus carboplatin-etoposide (CE) represents the new first-line treatment in extensive stage (ES)-Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) patients. This study aims at identifying the association of baseline and dynamic changes of cfDNA, Tumor Fraction (TF) and variant allele frequency (VAF) of tumor-related mutations with median (m) overall (OS) and progression free survival (PFS) in SCLC patients treated with ACE.
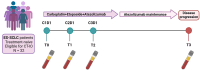
Materials and methods: This is a single-center prospective exploratory study including treatment-naive ES-SCLC patients eligible to first-line ACE. Liquid biopsies were longitudinally collected at baseline (T0), after cycle 1 (T1) and 2 (T2), at disease progression (T3). cfDNA Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) analysis was performed; genomic profiles and TF were inferred from shallow WGS (sWGS).
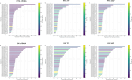
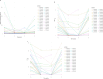
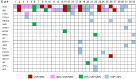
Results: Thirty-two patients were included; mPFS and mOS were 5.19 and 7.96 months, respectively. Higher T0 cfDNA (HR 1.44, 95% CI 1.17-1.77, p = 0.0006) and VAF (HR 2.6, 95% CI 1.36-4.93, p = 0.0039) were associated with risk of death; higher T0 cfDNA (HR 1.29, 95% CI 1.08-1.54, p = 0.0049), TF (HR 1.97, 95% CI 1.02-3.82, p = 0.044) and VAF (HR 2.32, 95% CI 1.22-4.42, p = 0.01) were predictors of risk of PD. Among the dynamic changes in the biomarkers under investigation, the association of 10-unit increase of VAF T0-T1 and T0-T2 with OS (HR 1.38, 95% CI 1.01-1.88, p = 0.043; HR 1.56, 95% CI 1.21-2.16, p = 0.008) and PFS (HR 1.69, 95% CI 1.18-2.43, p = 0.004; HR 1.81, 95% CI 1.22-2.70, p = 0.003) was estimated.
Conclusion: T0 and dynamic changes of cfDNA, TF and VAF may help physicians to stratify ES-SCLC patients receiving first-line ACE and to anticipate the clinical course of the disease.
Keywords: Atezolizumab; CfDNA; Chemoimmunotherapy; Liquid biopsy; SCLC.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study has been approved by Istituto Oncologico Veneto Ethical Committee (Cod. Int CESC IOV: 2021-85). All patients signed an informed consent form before enrollment. Consent for publication: All patient information has been anonymised and consent for publication of the current study was not required. All co-authors agreed for publication. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, et al. Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the united States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol Off J Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2006;24(28):4539–44. 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.4859. - PubMed
-
- Mascaux C, Paesmans M, Berghmans T, et al. A systematic review of the role of Etoposide and cisplatin in the chemotherapy of small cell lung cancer with methodology assessment and meta-analysis. Lung Cancer. 2000;30(1):23–36. 10.1016/s0169-5002(00)00127-6. - PubMed
-
- Paz-Ares L, Dvorkin M, Chen Y, et al. Durvalumab plus platinum-etoposide versus platinum-etoposide in first-line treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (CASPIAN): a randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet (London England). 2019;394(10212):1929–39. 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32222-6. - PubMed
-
- Horn L, Mansfield AS, Szczęsna A, et al. First-Line Atezolizumab plus chemotherapy in Extensive-Stage Small-Cell lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018;379(23):2220–9. 10.1056/NEJMoa1809064. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

