Focused cardiac ultrasound conducted by neurologists in patients with stroke: A validation study
- PMID: 40538151
- PMCID: PMC12181179
- DOI: 10.1177/23969873251345374
Focused cardiac ultrasound conducted by neurologists in patients with stroke: A validation study
Abstract
Introduction: Focused cardiac ultrasound (FoCUS) has a high diagnostic yield and a rapid theoretical learning curve. FoCUS can be applied in stroke assessments performed by stroke neurologists when a cardioembolic stroke is suspected.
Patients and methods: An international multicenter, prospective validation study was conducted to assess neurologists' ability to perform FoCUS. The FoCUS examination was defined as a simplified 2D transthoracic echocardiography. Neurologists and cardiologists performed the FoCUS independently and blinded. A twenty-question test evaluated neurologists' ability to recognize sources of cardioembolic stroke from recorded FoCUS studies.
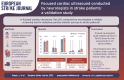
Results: A total of 432 paired studies involving 216 patients were conducted across 11 centers. No significant differences were found between neurologists and cardiologists in detecting: Left Ventricle (LV) dysfunction (7.4% vs 7.9%, p = 0.834), LV dilation (2.8% vs 2.3%, p = 0.766), VC collapsibility (7.2% vs 9.1%, p = 0.501), Right Ventricle dysfunction (0.9% vs 0.9%, p = 0.999), and pericardial effusion (0.5% vs 1.9%, p = 0.212). Cohen Kappa showed substantial agreement for LV dysfunction (0.640), moderate for LV dilation (0.589), and fair for VC collapsibility (0.226). Neurologists demonstrated 93.82% sensitivity and 92.92% specificity for detecting embolic sources. Success rate for LV akinesia was 88% (16/18), LV dysfunction 83% (15/18), complex aortic plaque 88% (16/18), and mitral stenosis 55% (10/18).
Discussion and conclusion: Properly trained neurologists can reliably perform FoCUS, particularly for assessing LV function and dilation, with better results in patients with favorable echocardiographic windows. While VC assessment requires further training, neurologists demonstrated high accuracy in identifying cardioembolic sources (over 90% of cases correctly identified). This study supports implementing standardized FoCUS training for neurologists through collaboration with cardiology specialists to enhance stroke diagnostics and management.
Keywords: Echocardiography; FoCUS; akinesia; left ventricle dysfunction; sources of stroke; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid, point-of-care antigen tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 22;7(7):CD013705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35866452 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
-
Duplex ultrasound for diagnosing symptomatic carotid stenosis in the extracranial segments.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 11;7(7):CD013172. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013172.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35815652 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of duplex ultrasound, magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography for the diagnosis and assessment of symptomatic, lower limb peripheral arterial disease.Health Technol Assess. 2007 May;11(20):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-184. doi: 10.3310/hta11200. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17462170
References
-
- Kolominsky-Rabas PL, Weber M, Gefeller O, et al. Epidemiology of ischemic stroke subtypes according to TOAST criteria: incidence, recurrence, and long-term survival in ischemic stroke subtypes: a population-based study. Stroke 2001; 32: 2735–2740. - PubMed
-
- Vaitkus PT, Barnathan ES. Embolic potential, prevention and management of mural thrombus complicating anterior myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 1993; 22: 1004–1009. - PubMed
-
- Mas JL, Arquizan C, Lamy C, et al. Recurrent cerebrovascular events associated with patent foramen ovale, atrial septal aneurysm, or both. N Engl J Med 2001; 345: 1740–1746. - PubMed
-
- Mitusch R, Doherty C, Wucherpfennig H, et al. Vascular events during follow-up in patients with aortic arch atherosclerosis. Stroke 1997; 28: 36–39. - PubMed
-
- Ntaios G, Michel P. Temporal distribution and magnitude of the vulnerability period around stroke depend on stroke subtype. Cerebrovasc Dis 2011; 32: 246–253. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

