Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease treatment: research progress
- PMID: 40538532
- PMCID: PMC12177340
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1565461
Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease treatment: research progress
Abstract
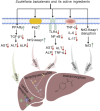
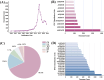
Metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD), previously known as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a common liver condition marked by excessive fat accumulation exceeding 5% in the liver without significant alcohol consumption. It is closely linked to metabolic disorders such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia, with a rising global prevalence projected to escalate from 25% to 56% over the next decade. The pathogenesis of MAFLD is multifaceted, involving insulin resistance, inflammation, and oxidative stress, with progressive symptoms that can lead to severe liver conditions including non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Current treatment options are limited, as established medications show variable efficacy and safety. Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi (S. baicalensis) a traditional Chinese herb rich in flavonoids, has garnered attention for its potential therapeutic effects on MAFLD. Its pharmacological activities, including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and lipid-regulating properties, position S. baicalensis as a promising candidate for MAFLD management. This article reviews the latest research progress of S. baicalensis in the treatment of MAFLD, explores its mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, and the development of related products, aiming to clarify the pathogenesis of MAFLD and promote the development of new treatment and prevention strategies based on traditional Chinese medicine.
Keywords: Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi; metabolic associated fatty liver disease; pharmacokinetics; pharmacological activities; production development.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Liu, Zhao, Liu, Dong, Lou, Huang, Li and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

