Polydatin-curcumin formulation alleviates CTD-ILD-like lung injury in mice via GABBR/PI3K/AKT/TGF-β pathway
- PMID: 40538533
- PMCID: PMC12176778
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1573525
Polydatin-curcumin formulation alleviates CTD-ILD-like lung injury in mice via GABBR/PI3K/AKT/TGF-β pathway
Abstract
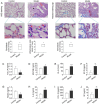
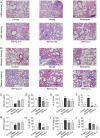
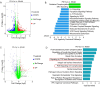
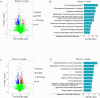
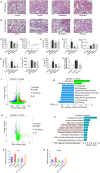
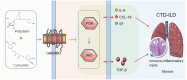
Connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease (CTD-ILD) is a systemic autoimmune disease with high morbidity and hazard, characterized by progressive pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. The monomer formulation of polydatin and curcumin (PD + Cur) for lung injury in CTD-ILD was optimized from Curcumae Longae Rhizoma (Curcuma Longa L.) and Polygoni Cuspidati Rhizoma Et Radix (Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc.). Mice with CTD-ILD-like lung injury were established by a single intratracheal drip of bleomycin. After intervening in model mice for 4 weeks, PD + Cur attenuated alveolar atrophy, fibrillar collagen formation, and thickened alveolar septa in the lung, improved serum biomarkers TOLLIP, MUC5B, KL-6, SP-D, and RCN3, and suppressed serum immunoinflammatory factors IL-6, CCL-18, and SF. The transcriptome sequencing showed that PD + Cur ameliorated CTD-ILD mainly by regulating aberrant immunoinflammation, which was further confirmed by proteomics that the PI3K/AKT/TGF-β pathway was a key pathway. Further, PD + Cur was found to affect amino acid metabolism in the serum significantly. The B-type receptor for GABA (GABBR) agonist baclofen was further found to attenuate CTD-ILD-like lung injury and modulate PI3K/AKT/TGF-β signaling. However, the inhibition of AKT, transforming growth factor beta receptor type 3 (TGFβR3), a key indicator downstream of PI3-kinase subunit p85-alpha (PI3KR1), by PD + Cur was reversed after intervention with the GABBR receptor inhibitor CGP52432. PD + Cur has an ameliorative effect on CTD-ILD-like lung injury by targeting GABBR to modulate the PI3K/AKT/TGF-β pathway.
Keywords: CTD-ILD; GABBR; PI3K/AKT/TGF-β; curcumin; polydatin.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Zhang, Lu, Wang, Li, Jin, Ma, Liu, Yang, Liu, Zhang, Gu, Deng, Wang and Meng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ba X., Wang H., Huang Y., Yan J., Han L., Lin W., et al. (2023). Simiao pill attenuates collagen-induced arthritis and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice by suppressing the JAK2/STAT3 and TGF-β/Smad2/3 signalling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 309, 116274. 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116274 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

