Case Report: Osimertinib-induced acute interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 40538542
- PMCID: PMC12176793
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1608733
Case Report: Osimertinib-induced acute interstitial lung disease
Abstract
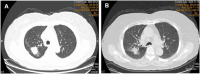
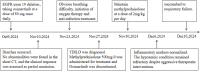
Osimertinib is a third-generation irreversible epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) that selectively targets EGFR-TKI-sensitive mutations, thereby inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Herein, we present a case of osimertinib-induced interstitial lung disease (ILD) in an 80-year-old woman with EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma. The patient was treated with osimertinib as first-line therapy for metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). On day 45 of treatment, she experienced acute onset of severe dyspnea, which rapidly progressed to diffuse bilateral pulmonary consolidation and profound hypoxemia. Despite discontinuation of osimertinib and administration of aggressive supportive care, her clinical condition continued to deteriorate, ultimately resulting in a fatal outcome. This case underscores the importance of monitoring respiratory symptoms in patients receiving EGFR-TKIs, promptly diagnosing ILD, and implementing early intervention to mitigate adverse outcomes.
Keywords: EGFR-TKI; adverse drug reaction; interstitial lung disease; lung cancer; osimertinib.
Copyright © 2025 Lin, Wu, Yu, Jiang, Yang and Xiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Front-line therapy for brain metastases and non-brain metastases in advanced epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell lung cancer: a network meta-analysis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2023 Nov 5;136(21):2551-2561. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002468. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023. PMID: 37160733 Free PMC article.
-
What is the optimal first-line regimen for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):620. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03438-3. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39695621 Free PMC article.
-
A Multicenter Open-Label Randomized Phase II Study of Osimertinib With and Without Ramucirumab in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Naïve EGFR-Mutant Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (RAMOSE trial).J Clin Oncol. 2025 Feb;43(4):403-411. doi: 10.1200/JCO.24.00533. Epub 2024 Oct 8. J Clin Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39378386 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Osimertinib-Induced Hepatitis Following Immunotherapy in a Patient with Lung Adenocarcinoma Harboring De Novo EGFR Exon 19 Deletion and T790M Mutations: A Case Report.Reports (MDPI). 2025 Jun 26;8(3):101. doi: 10.3390/reports8030101. Reports (MDPI). 2025. PMID: 40700234 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR-TKIs or EGFR-TKIs combination treatments for untreated advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC: a network meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2024 Nov 12;24(1):1390. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13168-8. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39533233 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous