Probiotics restore impaired spatial cognition and synaptic plasticity of prenatally-stressed male rats: focus on hippocampal and intestinal tight junctions
- PMID: 40538567
- PMCID: PMC12175731
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2025.100736
Probiotics restore impaired spatial cognition and synaptic plasticity of prenatally-stressed male rats: focus on hippocampal and intestinal tight junctions
Abstract
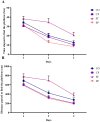
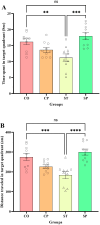
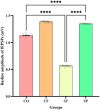
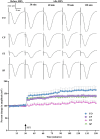
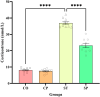
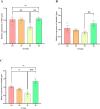
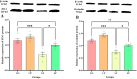
Bidirectional communication between the gut microbiota and the nervous system founded the gut-microbiota-brain axis, substantially affects numerous vital functions of the body. Stress, as the body's natural reaction to stressful situations, in turn, affects the functioning of various organs. Through evaluating long-term potentiation (LTP) and spatial memory assessment using the Morris water maze, we aimed to examine the effect of prenatal stress on the electrophysiological and behavioral aspects of hippocampus-dependent spatial memory. The relationship of the synaptic plasticity and learning and memory with the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and the integrity of blood-brain and intestinal barriers were also examined. The experimental subjects were introduced to probiotic treatment to assess how the supplementation influences stress-related alterations. The prenatal stress effectively impaired both LTP occurrence and behavioral function. It also led to disruption of blood-brain and gut barriers and increased serum level of corticosterone. The probiotic supplementation positively affected the synaptic plasticity and learning and memory. It also improved the integrity of both barriers and reduced the stress hormone corticosterone. Whereas there is a reverse relationship between stress and the hippocampus-dependent spatial memory, normal stress hormone, and the integrity of intestinal and brain barriers, the probiotic supplements improve all impairments. We conclude that the HPA axis plus the blood-brain and intestinal barriers play a role in hippocampus-dependent spatial memory that are substantially affected by the beneficial gut and probiotic bacteria.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis; Intestinal barrier; Learning and memory; Long-term potentiation; Probiotics; Stress.
© 2025 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Mahmoud Salami reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100004048Kashan University of Medical Sciences. If there are other authors, they declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Aghighi Bidgoli F., Salami M., Talaei S.A. Environmental enrichment restores impaired spatial memory and synaptic plasticity in prenatally stress exposed rats: the role of GABAergic neurotransmission. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2020;80(7):573–585. - PubMed
-
- Algamal M., Pearson A.J., Hahn-Townsend C., Burca I., Mullan M., Crawford F., Ojo J.O. Repeated unpredictable stress and social isolation induce chronic HPA axis dysfunction and persistent abnormal fear memory. Prog. Neuro Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatr. 2021;104 - PubMed
-
- Aoudia N., Rieu A., Briandet R., Deschamps J., Chluba J., Jego G., Garrido C., Guzzo J. Biofilms of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus fermentum: effect on stress responses, antagonistic effects on pathogen growth and immunomodulatory properties. Food Microbiol. 2016;53:51–59. - PubMed
-
- Barzegar M., Sajjadi F.S., Talaei S.A., Hamidi G., Salami M. Prenatal exposure to noise stress: anxiety, impaired spatial memory, and deteriorated hippocampal plasticity in postnatal life. Hippocampus (New York, N. Y.) 2015;25(2):187–196. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

