The role of fermented foods in maternal health during pregnancy and infant health during the first 1,000 days of life
- PMID: 40538587
- PMCID: PMC12176608
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1581723
The role of fermented foods in maternal health during pregnancy and infant health during the first 1,000 days of life
Abstract
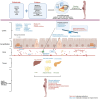
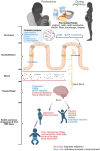
Fermented foods are a good source of nutrition, with microbiota and metabolites that can positively influence consumer health. With the increasingly negative health outcomes from using low-quality diets like processed diets, functional products like fermented foods are getting more attention than ever. All cultures of the world consume some kind of fermented foods. Extensive literature outlines positive health and clinical outcomes associated with fermented foods, yet most data are associative and lack longitudinal studies. This review explores the role of fermented foods during pregnancy and its subsequent impact on maternal and infant health, especially in the first 1,000 days of life. In this review, we have summarized the literature on fermented foods from preclinical and clinical studies that evaluated the impact of maternal consumption of fermented foods on mothers and offspring microbiota, immune system, and brain health outcomes. We also discussed existing knowledge gaps on maternal-child dyads and mechanistic studies needed to provide better scientific evidence to promote fermented foods consumption.
Keywords: brain; fermented foods; gut microbiota; immune system; infant; pregnancy.
Copyright © 2025 Pandiyan, Gurung, Mulakala, Ponniah and Yeruva.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

