Machine learning-based prediction of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: model development and clinical validation
- PMID: 40538804
- PMCID: PMC12176554
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1614657
Machine learning-based prediction of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: model development and clinical validation
Abstract
Background: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is a common and debilitating complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), significantly impacting patients' quality of life and increasing healthcare burdens. Early prediction and intervention are critical to mitigating its impact.
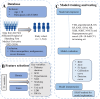
Methods: This study analyzed 1,544 diabetic patients from the First Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University, who were randomly divided into a training cohort (n = 1,082) and a testing cohort (n = 462) using a 7:3 split ratio. Feature selection was performed using both Boruta and LASSO algorithms, and the intersection of the selected variables was used as the final predictor set. Eight key predictors were identified from 23 variables, including diabetes duration, uric acid, HbA1c, NLR, smoking status, SCR, LDH, and hypertension. Nine machine learning models were developed and compared for DPN risk prediction.
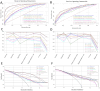
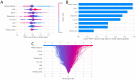
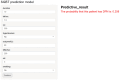
Results: Stochastic Gradient Boosting (SGBT) demonstrated the best performance (training AUC: 0.933, 95% CI: 0.921-0.946; testing AUC: 0.811, 95% CI: 0.776-0.843). Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) analysis provided interpretability, highlighting the clinical importance of diabetes duration and HbA1c among other predictors.
Conclusion: This study establishes a robust predictive tool for early DPN detection, laying the foundation for improved prevention and management strategies.
Keywords: clinical data; diabetic peripheral neuropathy; interpretable; machine learning; risk prediction model.
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Sun, Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Liu L, Bi B, Gui M, Zhang L, Ju F, Wang X, et al. Development and internal validation of an interpretable risk prediction model for diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: a single-centre retrospective cohort study in China. BMJ Open. (2025) 15:e092463. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-092463 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

