Association of organs-crosstalk with the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: cartilage as a key player
- PMID: 40538811
- PMCID: PMC12176559
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1593658
Association of organs-crosstalk with the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: cartilage as a key player
Abstract
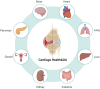
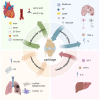
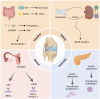
Degeneration of articular cartilage is the hallmark pathologic change in osteoarthritis (OA). Cartilage not only serves as a shock-absorbing structure for movement but is also regulated by organs other than bone, while chondrocytes secrete cytokines that influence these organs. The concept of organ axis refers to the regulatory pathways formed between organs via cytokine signaling. The communication network established between cartilage and other organs constitutes the cartilage-organ axis. Through this axis, these organs regulate articular chondrocyte proliferation and apoptosis. It is evident that chondrocytes play a central role in connecting various organs to the progression of OA, prompting interest in strategies to intervene in cartilage damage by modulating the organ axis. This review presents, for the first time, a system summarizing the effects of the extraosseous system on cartilage through various factors that alter OA progression. The aim is to fully elucidate the effects of different organs on cartilage, thus providing insights into the treatment of OA and systemic diseases.
Keywords: cartilage; chondrocyte; organs-crosstalk; osteoarthritis; therapeutic strategy.
Copyright © 2025 Qin, Di, Guo, Chen and Xiang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteolysis of the pericellular matrix: Pinpointing the role and involvement of matrix metalloproteinases in early osteoarthritic remodeling.Acta Biomater. 2024 Jun;181:297-307. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.05.002. Epub 2024 May 6. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 38710401
-
The role of autophagy in mitigating osteoarthritis progression via regulation of chondrocyte apoptosis: A review.Joint Bone Spine. 2024 May;91(3):105642. doi: 10.1016/j.jbspin.2023.105642. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Joint Bone Spine. 2024. PMID: 37739213 Review.
-
p-Synephrine Loaded by Injectable Gelma Hydrogel Ameliorates Cartilage Degeneration in Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Biol Pharm Bull. 2025;48(6):882-894. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b25-00139. Biol Pharm Bull. 2025. PMID: 40545361
-
Isoginkgetin protects chondrocytes and inhibits osteoarthritis through NF-κB and P21 signaling pathway.Mol Med. 2025 Jun 22;31(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01302-6. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40545529 Free PMC article.
-
Autologous chondrocyte implantation in the knee: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2017 Feb;21(6):1-294. doi: 10.3310/hta21060. Health Technol Assess. 2017. PMID: 28244303 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet (London England). (2024) 403:2133–61. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00757-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dasa V, Mihalko W, Rivadeneyra A, Urban J, Wickline A, Rogenmoser D, et al. Innovations in Genicular Outcomes Registry (IGOR): protocol for a real-world registry study of treatments for knee osteoarthritis. Ther Adv musculoskel Dis. (2024) 16:1759720x241304193. doi: 10.1177/1759720X241304193 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical