Targeting Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 Through PI3K-AKT-mTOR Signaling in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 40538996
- PMCID: PMC12177787
- DOI: 10.1002/oto2.70143
Targeting Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 Through PI3K-AKT-mTOR Signaling in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
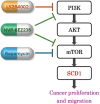
Objective: Stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 (SCD1) is a key enzyme in fatty acid metabolism and has been implicated in cancer progression, including head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-AKT-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway is a critical regulator of cellular metabolism and survival in cancer. This study investigates the crosstalk between SCD1 inhibition and the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway, highlighting the therapeutic potential of targeting SCD1 in HNSCC.
Study design: Basic science.
Setting: Laboratory.
Methods: Four HNSCC cell lines were utilized to evaluate the relationship between SCD1 and the mTOR signaling pathway. Cell viability was assessed following treatment with various mTOR inhibitors. The effect of AKT-mTOR signaling on SCD1 expression was examined through pharmacological inhibition and gene silencing approaches. Additionally, the impact of SCD1 knockdown on cell proliferation and survival was analyzed.
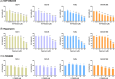
Results: mTOR inhibitors significantly reduced HNSCC cell viability and downregulated SCD1 expression in a dose-dependent manner. Inhibition of AKT, a key upstream effector of mTOR, also suppressed SCD1 expression, suggesting that SCD1 is regulated through the PI3K-AKT-mTOR axis. Silencing SCD1 independently impaired cancer cell growth and enhanced the cytotoxic effects of mTOR inhibitors, indicating a synergistic anticancer effect.
Conclusion: SCD1 is a downstream target of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway and contributes to HNSCC cell survival. Dual targeting of SCD1 and the mTOR signaling pathway represents a promising therapeutic strategy for HNSCC treatment. Further investigation is warranted to explore the clinical potential of SCD1 inhibitors in combination with mTOR-targeted therapies.
Keywords: PI3K‐AKT‐mTOR signaling; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC); lipid metabolism; stearoyl‐CoA desaturase 1 (SCD1); therapeutic target.
© 2025 The Author(s). OTO Open published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
IGF2BP1 promotes the progression of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by activating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway and inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition.World J Surg Oncol. 2025 Jul 14;23(1):277. doi: 10.1186/s12957-025-03929-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40660234 Free PMC article.
-
Classical swine fever virus utilizes stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1-mediated lipid metabolism to facilitate viral replication.J Virol. 2025 Jun 17;99(6):e0055125. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00551-25. Epub 2025 May 19. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40387378 Free PMC article.
-
Salidroside sensitizes Triple-negative breast cancer to ferroptosis by SCD1-mediated lipogenesis and NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy.J Adv Res. 2025 Aug;74:589-607. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.09.027. Epub 2024 Sep 29. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39353532 Free PMC article.
-
Current clinical regulation of PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR signalling in treatment of human cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015 Apr;141(4):671-89. doi: 10.1007/s00432-014-1803-3. Epub 2014 Aug 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25146530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in human malignancies; trend of current clinical trials.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov;149(16):15293-15310. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-05277-x. Epub 2023 Aug 18. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37594532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Igal RA. Stearoyl‐CoA desaturase‐1: a novel key player in the mechanisms of cell proliferation, programmed cell death and transformation to cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31(9):1509‐1515. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

