Low dose radiotherapy combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors induces ferroptosis in lung cancer via the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 axis
- PMID: 40539046
- PMCID: PMC12178237
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1558814
Low dose radiotherapy combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors induces ferroptosis in lung cancer via the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 axis
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) have revolutionized the therapeutic direction for lung cancer, yet their response rates remain unsatisfactory. Recently, the combination of ICI and low dose radiotherapy (LDR), a novel approach that effectively mobilizes innate and adaptive immunity, has gained interest among scientists. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms are not clearly elucidated.
Methods: The in vivo anti-tumor effects of LDR and ICI were measured in murine tumor models. The immune response and alterations in the tumor microenvironment were measured using flow cytometry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Cell viability and death were assessed using CCK-8 assays. Fluorescent probes and ELISA were used to assess ferroptosis induced by the combination therapy in vitro and in vivo. Western blotting and qPCR were performed to detect alterations in the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 pathway. Furthermore, a phase 1 clinical trial with a combined regimen of LDR and anti-PD-1 antibodies in patients with lung cancer was conducted.
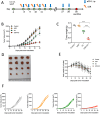
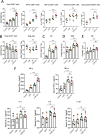
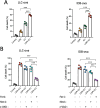
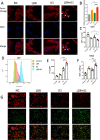
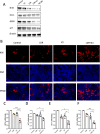
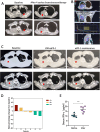
Results: The combined LDR and ICI regimen exhibited considerable anti-tumor effects in murine tumor models, promoting immune response and increasing the IFN-γ levels. In vitro data showed that LDR plus ICI induced ferroptosis in cancer cells by increasing reactive oxygen species and MDA levels, promoting Fe2+ accumulation, and suppressing GSH. Furthermore, ferroptosis induced by combination therapy was associated with suppression of the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 antioxidant axis. Importantly, a phase 1 clinical trial of the combination therapy showed promising efficacy in patients with lung cancer with chemoimmunotherapy resistance.
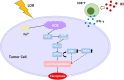
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that LDR plus ICI induces ferroptosis through the Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4 pathway, resulting in a significant anti-tumor effect and providing a combinatorial strategy to overcome lung cancer. However, this combined strategy merits further clinical investigation.
Keywords: Nrf2/HO-1/GPX4; chemoimmunotherapy-resistant; ferroptosis; immune checkpoint inhibitor; low dose radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2025 Luo, Zhi, Li, Xu, Zhu, Zhao, Ren, Wang and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

