The 6-kilodalton peptide 1 of the family Potyviridae: small in size but powerful in function
- PMID: 40539110
- PMCID: PMC12176749
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1605199
The 6-kilodalton peptide 1 of the family Potyviridae: small in size but powerful in function
Abstract
The Potyviridae family is one of the most economically significant groups of plant RNA viruses, causing severe yield losses in agriculturally important crops. Among the viral proteins encoded by potyviruses, the 6-kilodalton peptide 1 (6K1) has emerged as a critical, albeit poorly understood player in viral pathogenesis. Despite its small size, 6K1 exhibits diverse functions, including facilitating the assembly of viral replication complex (VRC), altering host membrane permeability as a viroporin, and interacting with host factors to promote infection. This review synthesizes current knowledge on 6K1, focusing on its structural characteristics, evolutionary conservation, molecular interactions, and potential as a target for antiviral strategies. We further discuss unresolved questions surrounding its putative ion channel activity, polyprotein processing dynamics, and functional parallels with animal virus viroporins. Understanding 6K1's multifunctionality provides new insights into viral infection mechanisms and opens avenues for novel disease control approaches.
Keywords: 6K1; Potyviridae; antiviral targets; membrane remodeling; viral replication complex; viroporin.
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Korxeelor, Wang, Chang, Jiang, Wu and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
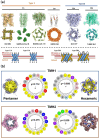
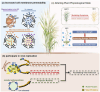
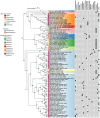

References
-
- Amin H. A., El Kammar H. F., Saied S. M., Soliman A. M. (2023). Effect of Bacillus subtilis on potato virus Y (PVY) disease resistance and growth promotion in potato plants. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 167, 743–758. doi: 10.1007/s10658-023-02774-0 - DOI
-
- Awaluddin F., Batubara I., Wahyudi S. T. (2023). Virtual screening of natural compounds against six protein receptors coded by the SARS-CoV-2 genome. Mol. Ther. 18, 147–158. doi: 10.20884/1.jm.2023.18.1.7884 - DOI
-
- Belabess Z., Tahiri A., Lahlali R. (2024). Contemporary perspectives on the global evolution of potato virus Y pathogen. Indian Phytopathol. 77, 13–34. doi: 10.1007/s42360-024-00709-1 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

