TIE1-dependent lymphatic vascular remodeling is mediated by its second tyrosine kinase domain
- PMID: 40539480
- PMCID: PMC12268172
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.204469
TIE1-dependent lymphatic vascular remodeling is mediated by its second tyrosine kinase domain
Abstract
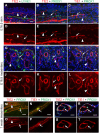
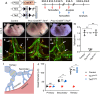
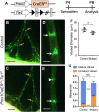
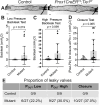
Mutations in ANG2 and TIE1 are associated with primary lymphedema in humans, but the mechanisms of ANG/TIE signaling in the lymphatic vasculature remain incompletely understood. We document that TIE2 is not detected in lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) before E14.5 but is expressed in collecting vessels from later embryonic stages, in contrast to robust TIE1 expression in all LECs from early stages. Accordingly, only LEC-specific deletion of Tie1 but not Tie2 resulted in defective lymphatic development and abnormal valve function. We discovered that defects of Tie1 lymphatic knockout mice were largely rescued by simultaneous loss of Foxo1. In addition, FOXC2 expression was abolished in Tie1-deficient lymphatics but restored by simultaneous loss of Foxo1, indicating that FOXO1, regulating FOXC2, might be a direct downstream effector of TIE1 signaling in the lymphatic system. Further, we generated point mutations in each tyrosine kinase domain of TIE1 and found that the second, but not the first, tyrosine kinase domain of TIE1 is essential for its function in the lymphatic system. Thus, our results suggest new avenues for manipulation of TIE1 signaling to enhance therapeutic lymphangiogenesis.
Keywords: FOXC2; FOXO1; Lymphatic system; Mouse; TIE1; TIE2; Tyrosine kinase domain.
© 2025. Published by The Company of Biologists.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Adams, R. H., Wilkinson, G. A., Weiss, C., Diella, F., Gale, N. W., Deutsch, U., Risau, W. and Klein, R. (1999). Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 13, 295-306. 10.1101/gad.13.3.295 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

