Mass Spectrometry-Driven Epitope Mapping: Application of Diethylpyrocarbonate Covalent Labeling for the Immunotherapeutic Target Programmed Cell Death Protein 1
- PMID: 40540218
- PMCID: PMC12232381
- DOI: 10.1021/jasms.5c00070
Mass Spectrometry-Driven Epitope Mapping: Application of Diethylpyrocarbonate Covalent Labeling for the Immunotherapeutic Target Programmed Cell Death Protein 1
Abstract
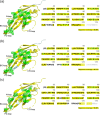
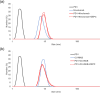
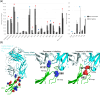
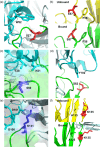
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have revolutionized immuno-oncology, with anti-programmed cell death protein 1 (PD1) mAbs emerging as key therapeutic agents in cancer treatment. This study presents the development and application of diethylpyrocarbonate (DEPC) covalent labeling-mass spectrometry (CL-MS) for detailed epitope mapping of anti-PD1 mAbs on PD1. By using DEPC CL-MS, we aimed to identify precise antibody binding sites on PD1 and benchmark its effectiveness against traditional X-ray crystallography. DEPC CL-MS offers high sensitivity and specificity while requiring less sample preparation and shorter analysis times, typically taking days or less, instead of months. PD1 was individually incubated with either nivolumab or a novel anti-human PD1 mAb (CU-MAB), followed by DEPC labeling, to assess DEPC modification extents under both binding and nonbinding conditions using bottom-up LC-MS/MS. Significant changes in DEPC modification at residues S27, S60, S62, S127, and K131 indicated binding sites and conformational shifts upon antibody interaction. These findings showed strong alignment with crystallography (PD1/nivolumab) and AlphaFold structural predictions (PD1/nivolumab and PD1/CU-MAB), highlighting the value of in-solution CL-MS for confirming AlphaFold predictions. This study underscores DEPC CL-MS as an efficient tool for epitope mapping, offering actionable insights into PD1-antibody interactions to drive therapeutic antibody development.
Keywords: Covalent Labeling; Diethylpyrocarbonate; Epitope Mapping; Immuno-Oncology; Mass Spectrometry; Monoclonal Antibodies; Nivolumab; PD1.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring preferred binding domains of IgG1 mAbs to multimodal adsorbents using a combined biophysics and simulation approach.Biotechnol Prog. 2024 Mar-Apr;40(2):e3415. doi: 10.1002/btpr.3415. Epub 2023 Dec 3. Biotechnol Prog. 2024. PMID: 38043031
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Screening of Amyloid Inhibitors via Covalent-Labeling Mass Spectrometry.Anal Chem. 2025 Jul 1;97(25):12989-12997. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.4c06418. Epub 2025 Jun 19. Anal Chem. 2025. PMID: 40537900
-
Rapid Mapping of Protein Binding Sites and Conformational Epitopes by Coupling Yeast Surface Display to Chemical Labeling and Deep Sequencing.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2937:111-123. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4591-8_6. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40593416
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang, T. ; Chen, J. ; Lu, Y. ; Xu, D. ; Yang, X. ; Ouyang, Z. . The Research Activities and Development Trends of Antineoplastics Targeting PD-1/PD-L1 Based on Scientometrics and Patentometrics. In 2022 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI); IEEE, 2022; pp 1687–1693. 10.1109/CSCI58124.2022.00300. - DOI
-
- ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline. The Common Technical Document for the Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use: Quality – M4Q(R1); 2002. https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/M4Q_R1_Guideline.pdf (accessed 2024-03-02).
-
- Guidelines on evaluation of biosimilars; World Health Organization, 2022. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/biologicals/annex-3---who-... (accessed 2024-03-02).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

