Design of Polyether sulfone flat-sheet membranes for multi-layered hemodiafiltration devices
- PMID: 40540465
- PMCID: PMC12180728
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324498
Design of Polyether sulfone flat-sheet membranes for multi-layered hemodiafiltration devices
Abstract
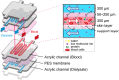
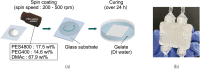
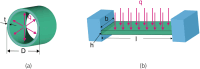
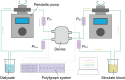
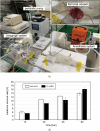
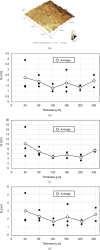
Multilayered hemodialysis devices enable blood flow without the need for an external pump, whereas hollow fiber-type devices require a pump due to significant pressure loss across the fibers. This highlights a key advantage of multilayered devices for implantable applications, where a simpler and lighter system reduces the burden on patients. This study investigates the mechanical strength and dialysis efficiency of polyether sulfone (PES) flat-sheet membranes for multilayered devices. PES membranes, with thicknesses ranging from 40 to 160 µm, were prepared using the liquid inversion method, with thickness controlled via spin coating. The mechanical strength of the membranes was tested following the ISO 8637-1:2017 protocol, and membranes thicker than 80 µm were experimentally verified to withstand pressures of up to 500 mmHg, making them suitable for dialysis applications. Furthermore, the study demonstrates the successful use of 80 µm membranes in both in vitro and ex vivo experiments with rats, identifying this thickness as optimal for multilayered dialysis devices.
Copyright: © 2025 Kono et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
No authors have competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sakai K. Technical determination of optimal dimensions of hollow fiber membranes for clinical dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 1989;4:73–7.
-
- Luo J, Wu C, Xu T, Wu Y. Diffusion dialysis-concept, principle and applications. Journal of Membrane Science. 2011;366(1–2):1–16. doi: 10.1016/j.memsci.2010.10.028 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

