Active peptides of TSP-1 inhibit retinal angiogenesis through the CD36 pathway in a rat model of choroidal neovascularization
- PMID: 40540467
- PMCID: PMC12180637
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325661
Active peptides of TSP-1 inhibit retinal angiogenesis through the CD36 pathway in a rat model of choroidal neovascularization
Abstract
Background: Choroidal neovascularization (CNV) is a key manifestation of intraocular neovascularization, and it is considered one of the main causes of blindness in ophthalmology. Additionally, multiple anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) drugs have been used as first-line treatment for CNV. However, several issues posed challenges to the anti-VEGF drugs, which were mainly composed of short duration of action, requirement for repeated injections, and complications. Thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1) is an endogenous protein that was found to regulate multiple biological processes within the body, and it has been proven to exhibit an inhibitory effect on neovascularization. Besides, the function of TSP-1 during the inhibition of neovascularization was currently considered to mainly focus on its type Ⅰ repeats (TSRs), which was attributed to the large molecular weight, complex structure, and possible unknown functions of TSP-1. Therefore, TSRs can be applied as targets and research directions for the further development and exploration of potential therapeutic drugs.
Objectives: Based on the type I repeats (TSRs) of thrombospondin-1 (TSP-1), amino acid sequences of different lengths were designed and synthesized in this study, named as VR-9 VR-10、VR-11、VR-12、VR-13. The objective was to explore the effects of the above five peptides on angiogenesis in Chori-retinal neovascularization, alongside the screening of the best peptides and the deep exploration into the underlying mechanism, aimed to provide a basis for the development and application of peptide drugs in the treatment of CNV.
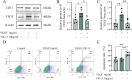
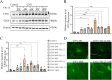
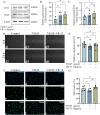
Methods: Wound healing, CCK-8, and 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) assays were employed to evaluate the proliferation and migration ability of cells. CRISPR-Cas9 technology was utilized to establish CD36 knockdown cell lines, alongside the conduction of qPCR to verify the efficiency of gene knockdown. The expression levels of VEGF and CD31 in RF/6A cells and rats were assessed by Western blot. Additionally, Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining was performed to examine the structural integrity of the rat retina, while Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-Dextran Cardiac Perfusion (FITC) labeling was used to observe the occurrence and development of choroidal neovascularization (CNV).
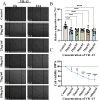
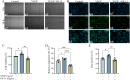
Results: According to the wound-healing and CCK-8 assays, VR-13 was the most effective in inhibiting the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells. Furthermore, VR-13 peptide effectively inhibited the pathological development of CNV without the detection of retinal toxicity in the rat CNV model.
Conclusions: Overall, it was found that VR-13 exhibit significant effects on the inducing of apoptosis and the inhibition of the progression of angiogenesis by regulating the expression of VEGF and CD31 via CD36 signaling pathway.
Copyright: © 2025 Li et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

