PPARγ inhibitors enhance the efficacy of statin therapy for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by directly inhibiting apoptosis and indirectly modulating lipoprotein subfractions
- PMID: 40540523
- PMCID: PMC12180619
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325190
PPARγ inhibitors enhance the efficacy of statin therapy for steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by directly inhibiting apoptosis and indirectly modulating lipoprotein subfractions
Abstract
Background: Steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head (SONFH) is a serious bone disease commonly seen in patients on long-term glucocorticoid therapy. Although statins have shown some efficacy in improving lipid metabolism, their efficacy in the treatment of SONFH remains limited. PPARγ inhibitors may enhance the efficacy of statins through several mechanisms. This study aims to investigate how PPARγ inhibitors may enhance the effects of statins in the treatment of SONFH by directly inhibiting apoptosis and indirectly modulating lipoprotein subfractions.
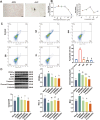
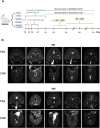
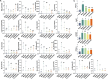
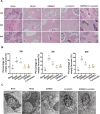
Methods: We first treated osteoblasts in vitro with high concentrations of hormones to simulate the SONFH environment. We then treated the cells with either the PPARγ inhibitor GW9662, the statin lovastatin, or a combination of both. We assessed cell proliferation and apoptosis using CCK-8, flow cytometry and Western blotting. We then established a SONFH rabbit model using high doses of methylprednisolone and lipopolysaccharide. The rabbits were randomly divided into four groups: control group, lovastatin group, GW9662 group and combination therapy group. We observed hip joint MRI before treatment, after 4 weeks of treatment, and 4 weeks after stopping treatment. We performed hematoxylin-eosin staining of the femoral head and analysed serum lipoprotein subfractions using VAP technology. In addition, we used quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) to analyse the expression of genes related to lipid metabolism at week 3.
Results: In vitro experiments showed that both GW9662 and lovastatin effectively inhibited hormone-induced apoptosis. In the animal studies, imaging and pathological results showed that the progression of SONFH was slower in the combination therapy group than in the other groups. VAP analysis showed that the lovastatin group had disturbed lipoprotein subfractions at the fourth week after stopping treatment, while the combination therapy group had more stable lipoprotein subfractions.
Conclusion: PPARγ inhibitors significantly enhance the efficacy of statins in the treatment of SONFH by directly inhibiting apoptosis and indirectly modulating lipoprotein subfractions. These findings provide new insights into the clinical management of SONFH and suggest that combination therapy may be an effective strategy.
Copyright: © 2025 Chen et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Yu X, Dou S, Lu L, Wang M, Li Z, Wang D. Relationship between lipid metabolism, coagulation and other blood indices and etiology and staging of non-traumatic femoral head necrosis: a multivariate logistic regression-based analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024;19(1):251. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04715-x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

