Substance Use Disorder Treatment Outcomes: Methodological Overview of Metrics and Criteria
- PMID: 40540529
- PMCID: PMC12180564
- DOI: 10.1002/mpr.70027
Substance Use Disorder Treatment Outcomes: Methodological Overview of Metrics and Criteria
Abstract
Aim: The heterogeneous metrics and criteria used to assess the effectiveness of substance use disorders treatment hinders cross-study comparisons. This review aims to parse such heterogeneity by analysing the operational definitions of variables used to derive metrics and outcome criteria, contributing to the standardisation process.
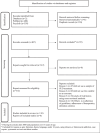
Methods: We conducted a systematic review in PubMed and PsycINFO between January 2000 and October 2023. We included published studies on substance use disorders that featured at least one of seven 'a priori' defined variables commonly used to obtain metrics and criteria for treatment effectiveness. The review process and reporting followed Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines.
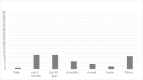
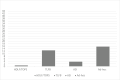
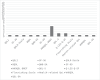
Results: Were identified three areas that can be used to define metrics and criteria associated with treatment outcome: as 'substance use' (abstinence and relapses), 'treatment process' (readmission, dropout, retention, and adherence) and 'general wellbeing' (quality of life). Operational definitions and metrics and criteria used were overall inconsistent.
Conclusions: The establishment of guidelines for evaluation of treatment outcomes is imperative, as heterogeneity is still present in the literature. We recommend that future trials provide outcomes metrics relevant to the identified categories, and that standardisation efforts continue toward harmonised criteria to report and interpret those metrics.
Keywords: effectiveness; measures; outcomes; substance use disorder; systematic review; treatment outcome.
© 2025 The Author(s). International Journal of Methods in Psychiatric Research published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- * Abdollahi, M. , and Haghayegh S. A.. 2020. “Efficacy of Group Therapy Based on 12‐Step Approach of Narcotics Anonymous on Self‐Control and Quality of Life in People With Substance Use Disorder Diagnosis During Recovery.” Practice in Clinical Psychology 8, no. 1: 17–26. 10.32598/jpcp.8.1.19. - DOI
-
- Adinoff, B. , Talmadge C., Williams M. J., Schreffler E., Jackley P. K., and Krebaum S. R.. 2010. “Time to Relapse Questionnaire (TRQ): A Measure of Sudden Relapse in Substance Dependence.” American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 36, no. 3: 140–149. 10.3109/00952991003736363. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- * Aldemir, E. , Berk G., and Çoşkunol H.. 2018. “The Effects of the Addiction Programme of Probation on Treatment Motivation, Abstinence and Quality of Life: A Comparative Study With Motivational Interviewing and Individual Intervention.” Nöropsikiyatri Arsivi 55: 261–270. 10.5152/npa.2017.19440. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aldridge, A. , Zarkin G. A., Dowd W., and Bray J. W.. 2016. “The Relationship Between the End of Treatment Alcohol Use and Subsequent Health Care Costs: Do Heavy Drinking Days Predict Higher Health Care Costs.” Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 40, no. 5: 1122–1128. 10.1111/acer.13054. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical