Effects of K-wire diameter and insertion angle on femoral bone medial closing-wedge osteotomies: a finite element study
- PMID: 40541981
- PMCID: PMC12181366
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-04260-5
Effects of K-wire diameter and insertion angle on femoral bone medial closing-wedge osteotomies: a finite element study
Abstract
Medial closing-wedge surgery for distal femoral osteotomy is employed to correct genu valgum by correcting coronal plane malalignment. This procedure involves pre-surgery planning, creating a wedge incision, performing the osteotomy, and stabilizing with plates and screws. However, hinge fractures during wedge closure present significant challenges, often necessitating revisions. Contemporary solutions have explored the use of k-wires, and this study investigates their biomechanical implications. The interplay between k-wire insertion angle and diameter, often overlooked in existing literature, is a critical determinant of their efficacy in achieving successful osteotomies, highlighting gaps in our understanding of these key parameters. We hypothesize that k-wire mechanics vary with insertion angle and diameter. This study examines the introduction of k-wires at different angles (30°, 45°, and 60°) and diameters (1.6, 1.8, and 2 mm) using computed tomography-based finite element models to assess structural integrity during femoral medial closing-wedge osteotomy. Results reveal angle-dependent stress variations, with 60° configurations exhibiting favorable patterns that reduce tensile and compressive loads and plastic deformation-crucial in preventing hinge fractures. Diameter variations show no significant differences in stresses or system stiffness. It was also found that while angle significantly affects stresses, lower diameters appear optimal only in combination with higher angles. Comparative analysis of k-wire systems with a naïve model demonstrates that k-wires at a 60° angle reduce tensile and compressive loadings and plastically deformed volume fractions, thus lowering fracture risk. This study underscores the importance of optimizing k-wire placement and configuration, particularly highlighting the significance of the insertion angle. Future research should expand the range of angles and diameters tested and examine different femoral geometries and osteotomy angles to provide a more comprehensive understanding and enhanced clinical application.
Keywords: Biomechanics; Digital twin; Hinge fracture prevention; In silico; K-wire; Orthopedics; Stress and strain analysis; Structural stability; Surgical optimization.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval statement: Experimental protocol and data analysis was approved by the local ethics committee of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Germany. We ensured that our work adhered to ethical guidelines and complied with local laws and regulations. Additionally, our study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, ensuring that the rights and well-being of the participant were protected throughout the research process.
Figures
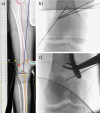


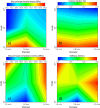

References
-
- Hendrikx, F. R. & Verdonk, P. Medial closing-wedge distal femoral osteotomy: surgical technique. Osteotomy About Knee: Comprehensive Guide10.1007/978-3-030-49055-3_11 (2020).
-
- Hegarty, P., Getgood, A. Osteotomy: Patient evaluation and indications, in Knee Arthroscopy and Knee Preservation Surgery, S.L. Sherman, et al., Editors. 2023, Springer International Publishing: Cham. p. 1–21.10.1007/978-3-030-82869-1_45-1
-
- D’Arienzo, A., et al., Biological Reconstruction of the Distal Femur—I: Massive Allograft and Inlaid Free Vascular Fibula, in Orthopedic Surgical Oncology For Bone Tumors : A Case Study Atlas, H. Özger, et al., Editors. 2022, Springer International Publishing: Cham. p. 191–202. 10.1007/978-3-030-73327-8_19
-
- Fujita, K. et al. Influence of lateral hinge fractures on biplanar medial closing-wedge distal femoral osteotomy for valgus knee: A new classification of lateral hinge fracture. Arch. Orthop. Trauma Surg.143(3), 1175–1183. 10.1007/s00402-021-04212-4 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

