One step synthesis of Ag nanoparticles incorporated PVA nanocomposite via plasma reduction route
- PMID: 40541985
- PMCID: PMC12181264
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-03700-6
One step synthesis of Ag nanoparticles incorporated PVA nanocomposite via plasma reduction route
Abstract
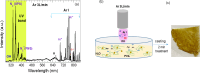
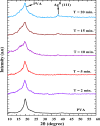
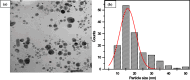
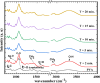
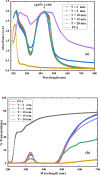
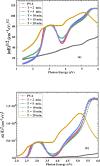
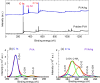
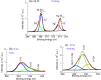
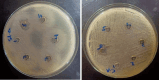
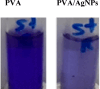
PVA/Ag nanocomposite films were synthesized via a one-step plasma-solution reduction method with varying processing times. Following synthesis, the PVA/Ag NP solutions were cast to form films, which were subsequently characterized by TEM, XRD, FTIR, XPS, UV-Vis, and Raman spectroscopy. Antimicrobial activity was evaluated using an agar diffusion test. TEM analysis confirmed the presence of Ag NPs with diverse sizes and shapes, averaging around 16.1 nm. XRD analysis showed a distinct peak at 2θ = 38°, corresponding to the Ag (111) plane in films synthesized at 10, 15, and 20 min, indicating the formation of crystalline Ag NPs. XPS results demonstrated an increased O/C ratio in plasma-synthesized PVA/Ag nanocomposite films, along with a new peak at 369.15 eV attributed to the Ag 3d orbital, confirming the presence of Ag NPs within the PVA matrix. FTIR spectra further suggested the formation of coordinate bonds between Ag NPs and PVA polymer chains. UV-Vis analysis revealed a localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) peak at approximately 425 nm, with a redshift to 445 nm at a longer processing time (20 min). This suggests alterations in NP size or interaction with the matrix. The optical bandgap of PVA/AgNP films decreased with longer plasma processing time, accompanied by increased film opacity. Raman analysis highlighted the potential use of PVA/Ag NP films (synthesized at 5 min) as substrates for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). The PVA/Ag NP composite synthesized at a plasma processing time of 20 min exhibited considerable antibacterial activity against S. aureus and C. albicans. Also, the percentage of biofilm inhibition of S. aureus was 65%, compared to the control. Collectively, these findings suggest that plasma-synthesized PVA/Ag NP nanocomposite films are promising candidates for various applications, including optical devices, food packaging, SERS, and wound dressings.
Keywords: Ag NPs; Antimicrobial properties; Nanocomposites; Opacity; Optical energy gap; PVA; SERS; XPS.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: The research is not involving the studies on human or their data.
Figures

References
-
- Liu, C., Li, F., Ma, L.-P. & Cheng, H.-M. Advanced materials for energy storage. Adv. Mater.22, E28–E62 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Sardar, R., Hwang, H. & Kwon, S. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Nanoscale8(7), 4136–4150 (2016).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

