Ellipsoid zone reflectivity as a functional imaging biomarker for age-related macular degeneration: a MACUSTAR study report
- PMID: 40542004
- PMCID: PMC12181357
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00735-7
Ellipsoid zone reflectivity as a functional imaging biomarker for age-related macular degeneration: a MACUSTAR study report
Abstract
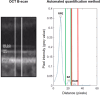
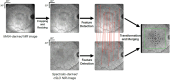
This study evaluated the functional relevance of relative ellipsoid zone reflectivity (rEZR) on spectral-domain optical coherence tomography as a structural biomarker for retinal integrity, focusing on its association with retinal function. Participants with age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and controls from the MACUSTAR study underwent functional testing, including mesopic fundus-controlled perimetry, best-corrected visual acuity, low-luminance visual acuity, low-luminance deficit, Moorfields Acuity Test, and Pelli-Robson contrast sensitivity, along with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography imaging. Structural and functional data were analyzed globally and spatially aligned for topographic analysis. Linear-mixed effects models, adjusted for age, sex, and eccentricity of the rEZR, assessed associations between rEZR and functional metrics. A total of 275 eyes (early AMD, n = 34; intermediate AMD, n = 152; late AMD, n = 36; controls, n = 53) from 275 participants (mean ± standard deviation age: 71.1 ± 7.2 years; 63.3% female) were included. In global analyses, rEZR was associated with the mean average threshold in mesopic fundus-controlled perimetry (coefficient estimate 0.0492, 95% confidence interval 0.0190-0.0794, p = 0.0015), low-luminance visual acuity (coefficient estimate - 0.0015, 95% confidence interval - 0.0026 to - 0.0004, p = 0.0092), Moorfields Acuity Test (coefficient estimate 0.0092, 95% confidence interval - 0.0022 to - 0.0001, p = 0.0285), and Pelli-Robson contrast sensitivity (coefficient estimate 0.0030, 95% confidence interval 0.0015-0.0045, p = 0.0001). Topographic analysis further revealed an association of rEZR with mesopic retinal sensitivity (coefficient estimate 0.0065, 95% confidence interval 0.0026-0.0104, p < 0.0001). Higher outer retinal reflectivity is linked to better retinal function in AMD and controls, supporting its potential as a biomarker for retinal integrity and function.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

