A novel nanoparticle glutathione and Lepidium sativum treatment for gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats
- PMID: 40542040
- PMCID: PMC12181309
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05385-3
A novel nanoparticle glutathione and Lepidium sativum treatment for gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats
Abstract
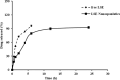
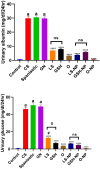
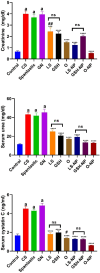
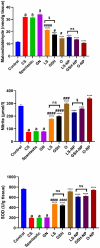
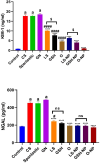
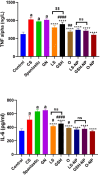
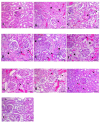
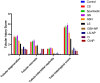
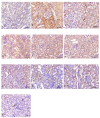
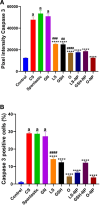
Acute renal failure (ARF) is a sudden, significant, and often reversible decline in kidney function, with 25% of all hospital-administered pharmaceuticals potentially causing nephrotoxicity. The study investigates the effectiveness of a novel nanoparticle (NP) formulation of glutathione (GSH) and Lepidium sativum (LS) in improving therapeutic outcomes in a rat model of ARF. Sixty adult male albino rats were allocated into ten groups, comprising six rats each, for the study. ARF was created by daily gentamicin (GN) administration for seven consecutive days and various treatment protocols, including chitosan (CS) NPs, spanlastics NPs, as well as conventional, NP formulations of GSH, LS, and their respective combinations. The effect was evaluated through various tests, and properties of nanoparticles were confirmed through characterization processes. The NP compositions markedly enhanced renal function, as seen by reduced urine concentrations of albumin and glucose. Furthermore, the serum concentrations of creatinine (SCr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and cystatin C were decreased. Tissue concentrations of nitrite, superoxide dismutase (SOD), and malondialdehyde (MDA), as markers of oxidative stress, were enhanced by both conventional and NP formulations. Additionally, they decreased inflammatory markers such as kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6). Histological analysis and immunohistochemical testing revealed that the combination therapy, particularly with the nanoforms, significantly decreased caspase 3 cellular immunoexpression, a sign of kidney cellular damage. The findings show that the ARF renal damage is considerably reduced when NPs containing GSH and LS are administered together. The study suggests a promising pharmacological approach for enhancing kidney regeneration and preserving renal function, potentially aiding in new therapeutic interventions for ARF treatment.
Keywords: ARF; Caspase 3; Gentamicin; IL-6; LS; Nanoparticles.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The work was conducted in accordance with the ethical treatment criteria for laboratory animals, as specified in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and the ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. The Institutional Animal Ethics Committee granted prior consent (approval no. 06/2024/0277). Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel pharmacological strategy using nanoparticles with glutathione and virgin coconut oil to treat gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jan;398(1):933-950. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03303-4. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39093465 Free PMC article.
-
Nephroprotective Effects of Curcumin in Murine Models of Focal and Segmental Glomerulosclerosis.Pharmacology. 2025;110(4):221-230. doi: 10.1159/000543293. Epub 2025 Jan 8. Pharmacology. 2025. PMID: 39778541
-
Naringin mitigated doxorubicin-induced kidney injury by the reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation with a synergistic anticancer effect.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Jun 23;26(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00947-7. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40551188 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
References
-
- Jose, S. P. et al. Nephro-protective effect of a novel formulation of unopened coconut inflorescence sap powder on gentamicin induced renal damage by modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory markers. Biomed. Pharmacother.85, 128–135 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Sabra, M. S., Allam, E. A., El-Aal, M. A., Hassan, N. H., Mostafa, A.-H. M. & Ahmed, A. A. A novel pharmacological strategy using nanoparticles with glutathione and virgin coconut oil to treat gentamicin-induced acute renal failure in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1–18 (2024). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Murphy, C., Barrington-White, H., Pomeranc, A. & Ghalli, F. MMF as immunosuppressive therapy in IgA nephropathy. Adv. J. Urol. Nephrol.5, 36–43 (2023).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

