Tuning surface properties of thiophene-based thin films on glass substrates for cancer cell adhesion, drug release control, and computational analysis
- PMID: 40542057
- PMCID: PMC12181427
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-05691-w
Tuning surface properties of thiophene-based thin films on glass substrates for cancer cell adhesion, drug release control, and computational analysis
Abstract
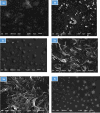
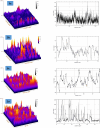
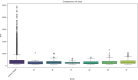
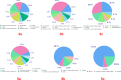
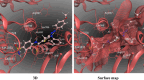
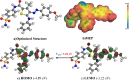
This study explores the potential of six novel thiophene derivative thin films (THIOs) for reducing cancer cell adhesion and enhancing controlled drug release on inert glass substrates. Thiophene derivatives 3a-c and 5a-c were synthesized and characterized using IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, and elemental analysis before being spin-coated onto glass to form thin films. SEM analysis and roughness measurements were used to assess their structural and functional properties. Biological evaluations demonstrated that the films significantly reduced HepG2 liver cancer cell adhesion (~ 78% decrease vs. control) and enabled controlled drug release, validated through the Korsmeyer-Peppas model (R2 > 0.99). Theoretical studies, including in-silico target prediction, molecular docking with JAK1 (PDB: 4E4L), and DFT calculations, provided insights into the electronic properties and chemical reactivity of these compounds. Notably, compound 5b exhibited the best binding energy (-7.59 kcal/mol) within the JAK1 pocket, aligning with its observed apoptotic behavior in cell culture. DFT calculations further revealed that 5b had the lowest calculated energy values; -4.89 eV (HOMO) and - 3.22 eV (LUMO), and the energy gap was found to be 1.66 eV, supporting its role in JAK1 inhibition and cancer cell adhesion reduction. These findings underscore the promise of thiophene derivatives in biomedical applications, potentially leading to safer surgical procedures and more effective localized drug delivery systems.
Keywords: Cancer adhesion; DFT; Docking; Drug release; Hepatocellular; Thin film; Thin film glass; Thiophene.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of paclitaxel, docetaxel, gemcitabine and vinorelbine in non-small-cell lung cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(32):1-195. doi: 10.3310/hta5320. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 12065068
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Exploring Type II Diabetes Inhibitors from Genus Daphne Plant-species: An Integrated Computational Study.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025;28(8):1413-1442. doi: 10.2174/0113862073262227231005074024. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2025. PMID: 38584562
-
A systematic review and economic evaluation of epoetin alpha, epoetin beta and darbepoetin alpha in anaemia associated with cancer, especially that attributable to cancer treatment.Health Technol Assess. 2007 Apr;11(13):1-202, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta11130. Health Technol Assess. 2007. PMID: 17408534
References
-
- Giuliani, M. et al. Can breast cancer biopsy influence Sentinel lymph node status?? Clin. Breast. Cancer.16 (6), e153–e157 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Sennerstam, R. B., Franzén, B. S. H., Wiksell, H. O. T. & Auer, G. U. Core-needle biopsy of breast cancer is associated with a higher rate of distant metastases 5 to 15 years after diagnosis than FNA biopsy. Cancer Cytopathol.125 (10), 748–756 (2017). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

