Vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids attenuate MSG-induced neurodegeneration by modulating tau pathology, neuroinflammation, and VDR expression in rats
- PMID: 40542117
- PMCID: PMC12181329
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06109-3
Vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids attenuate MSG-induced neurodegeneration by modulating tau pathology, neuroinflammation, and VDR expression in rats
Abstract
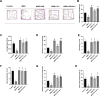
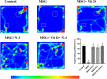
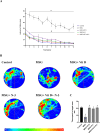
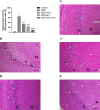
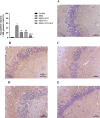
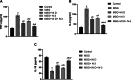
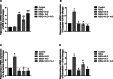
Monosodium glutamate (MSG)-induced excitotoxicity is a major factor contributing to cognitive decline and neurodegeneration. Given the well-established roles of vitamin D (Vit D) and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (N-3 PUFAs), especially eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), in neuroprotection, the present study aimed at analyzing their possible neuroprotective efficacy against MSG-induced neurotoxicity in rats, concerning the behavioral performance, hippocampal histological integrity, and pathological protein accumulation, along with determination of the inflammatory marker levels and mRNA expression of vitamin D receptors (VDR) and other neurodegeneration-related genes. Fifty male Sprague Dawley rats were randomly allocated to a control, an MSG, and three treatment groups that received MSG and either Vit D or N-3 PUFA supplements in combinations or alone for 4 weeks. At the end of the study, five behavioral tests were conducted to assess cognitive functions, motor activity, and anxiety-related behaviors, and hippocampal tissues were analyzed for tau pathology, neuroinflammation, expression of VDR, and neurodegeneration-related markers. The results demonstrated that supplementation with Vit D (1 mcg/kg) and N-3 PUFAs (300 mg/kg EPA + DHA) profoundly attenuated MSG-induced neurodegeneration. The combined therapy decreased neuronal damage caused by MSG by 87% and tau pathology by 83%. The combined treatment further suppressed pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α: 52%; IL-6: 65%) and elevated anti-inflammatory IL-10 by 2.8-fold, demonstrating a dual anti-inflammatory action. A major upregulation of hippocampal VDR by 4.6-fold was noted, with stabilization of calcium homeostasis and normalization of caspase-3 and α-synuclein expression. Our findings confirm that Vit D and N-3 PUFAs exhibit substantial synergistic neuroprotective abilities that might be mediated through synergistic VDR upregulation, providing a promising dietary intervention against MSG-induced excitotoxicity and highlighting their broader implications for supporting cognitive health and mitigating the adverse effects of other neurotoxins.
Keywords: MSG; Neuroinflammation; Omega-3 PUFAs; Tau pathology; VDRs; Vitamin D.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics approval: The experimental protocol was approved by the Mansoura University Animal Care and Use Committee (MU-ACUC), Mansoura, Egypt, approval code: MU-ACUC (MED.PhD.23.06.2). All applicable international, national, and institutional ethical guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures were performed under ARRIVE guidelines and followed the U.K. Animals ACT, of 1986. Consent for publication: All authors have read and approved the final manuscript for publication.
Figures

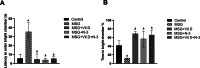
References
-
- Timoney, N. & Miller, B. Injury to the Developing Nervous System. In:The Encyclopedia of Child and Adolescent Development 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119171492.wecad014 (2020).
-
- Appaiah, K. M. in In Ensuring Global Food Safety. (eds Christine, E., Boisrobert, A. & Stjepanovic) Academic, 217–226. (2010).
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

