Exploring circulating cell-free DNA as a biomarker and as an inducer of AIM2-inflammasome-mediated inflammation in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm
- PMID: 40542152
- PMCID: PMC12181305
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-06220-5
Exploring circulating cell-free DNA as a biomarker and as an inducer of AIM2-inflammasome-mediated inflammation in patients with abdominal aortic aneurysm
Abstract
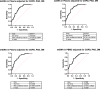
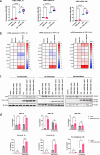
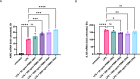
Circulating cell-free (cf) DNA in blood plasma is considered a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker of tissue damage and could be a driver of chronic inflammation by stimulating the innate immune response via activation of inflammasomes. Increased AIM2-inflammasome activity in the aortic wall is associated with abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). We here hypothesized that cfDNAs are elevated in the plasma of AAA patients and are associated with chronic inflammation. Single strand (ss)DNA, double strand (ds)DNA and mitochondrial (mt)DNA levels were explored in plasma and leucocytes from 93 AAA patients, 89 controls (non-AAA patients) and 10 healthy subjects, using fluorescence-based quantification and real-time qPCR, respectively. To analyse inflammasome activation by cfDNA, differentiated THP-1 macrophages were primed with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and then stimulated for one, six or 24 h with DNA extracted from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) of AAA patients. Our analysis revealed significantly increased levels of ssDNA, dsDNA and mtDNA levels in plasma from AAA patients compared with non-AAA patients and healthy subjects. In addition, the mtDNA copy number was significantly higher in PBMC from AAA patients. Stimulation of THP-1 cells with PBMC-DNA resulted in increased expression of inflammasome genes, especially the DNA sensors AIM2 and IFI16. At early time points, PBMC-DNA stimulated THP-1 showed significantly increased apoptosis-associated speck-like protein with a CARD (ASC) and Pro-Interleukin-1β protein levels compared to untreated or only LPS-primed cells, resulting in the formation of significantly more ASC specks after 24 h, a sign of inflammasome activation. We conclude from our data that cfDNA of AAA patients triggers a proinflammatory response in macrophages by activating the AIM2 inflammasome and thus could be a driving force for the chronic inflammation observed in these patients.
Keywords: AIM2; Abdominal aortic aneurysm; Biomarker; Cell free DNA; Inflammasome; Proinflammatory response; THP-1 cells; mtDNA.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interest: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval and consent to participate: The study was conducted according to the Code of Ethics of the World Medical Association (Declaration of Helsinki). All participants gave their written informed consent to the study, which was approved by the ethical committee of the University of Heidelberg (S-091/2021) and (S-310/2013 “Etablierung einer humanen vaskulären Biomaterialbank (VBBH) an der Klinik für Gefäßchirurgie und endovaskuläre Chirurgie der Universitätsklinik Heidelberg), and amendments.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

