Modeling Emotional Arousal With Turbulence Measured by EEG
- PMID: 40542499
- PMCID: PMC12181742
- DOI: 10.1111/psyp.70093
Modeling Emotional Arousal With Turbulence Measured by EEG
Abstract
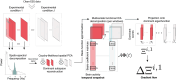
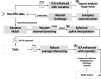
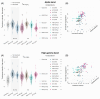
Turbulence-like dynamics in brain activity have been proposed as a signature of systems operating near criticality, and may reflect changes in neuronal function associated with emotional states. In this paper, we hypothesize that motor behavior linked to emotional expression modulates turbulence, reflecting a shift towards more streamlined brain dynamics characteristic of emotional motor control. We assessed EEG turbulence in 30 healthy participants in a motor paradigm varying in both task demand and degree of emotionality. Conditions included singing, swaying, responding to a virtual conductor of variable expressivity, having your own body movements mirrored by a virtual agent, and combinations thereof. Results showed an inverse relation of turbulence intensity in the alpha range to both degree of movement and perceived level of task emotionality, which was also true for the high gamma range, but to a lesser extent. When factoring in task demand, the effect of level of emotionality in the alpha range deteriorated. This is physiological evidence for why physical arousal is likely to increase the level of perceived emotional engagement or even be misinterpreted as such. Our findings suggest high gamma activity is a more accurate indicator of emotionality during motor tasks and can be key to differentiating EEG signatures of emotional motor control, which has been shown to be partly autonomous from voluntary motor control.
Keywords: criticality; emotional motor control; functional data; immersive VR; mind–brain–body; multisensory processing; naturalistic neuroscience.
© 2025 The Author(s). Psychophysiology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Society for Psychophysiological Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

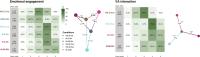
Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Comparison of cellulose, modified cellulose and synthetic membranes in the haemodialysis of patients with end-stage renal disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003234. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003234.pub2. PMID: 11687058 Updated.
References
-
- Arroyo, S. , Lesser R. P., Gordon B., Uematsu S., Jackson D., and Webber R.. 1993. “Functional Significance of the Mu Rhythm of Human Cortex: An Electrophysiologic Study With Subdural Electrodes.” Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology 87: 76–87. 10.1016/0013-4694(93)90114-B. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

