More Than Three Decades After Discovery of the Neuroprotective Effect of PACAP, What Is Still Preventing Its Clinical Use?
- PMID: 40542938
- PMCID: PMC12182478
- DOI: 10.1007/s12031-025-02366-z
More Than Three Decades After Discovery of the Neuroprotective Effect of PACAP, What Is Still Preventing Its Clinical Use?
Abstract
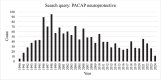
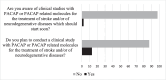
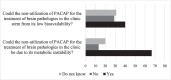
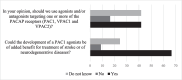
Discovered in 1989, pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP) is a neuropeptide with strong neuroprotective properties, as shown in various neurodegenerative preclinical models of Parkinson, Alzheimer, or Huntington diseases. PACAP neuroprotection has also been reported in animal models of cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain injury. The neuroprotective effect of PACAP occurs through its capacity to modulate most of the multiphasic aspects of neuronal diseases, such as oxidative stress, neuronal cell death, and inflammation. However, more than three decades after its discovery, and although PACAP neurotrophic and neuroprotective activities have now been largely documented, its clinical use is still awaited. Thus, the aim of this manuscript is to discuss the main reasons which limit the use of PACAP as a therapeutic agent for the treatment of neuronal diseases. To achieve this objective, an opinion survey has been conducted among experts in the field of PACAP, and a bibliographic investigation was carried out.
Keywords: Clinical use; Neurodegenerative diseases; Neuroprotection; PACAP.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PACAP glycosides promote cell outgrowth in vitro and reduce infarct size after stroke in a preclinical model.Neurosci Lett. 2024 Jul 27;836:137883. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2024.137883. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Neurosci Lett. 2024. PMID: 38914278 Free PMC article.
-
Single-incision sling operations for urinary incontinence in women.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 26;7(7):CD008709. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008709.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Oct 27;10:CD008709. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008709.pub4. PMID: 28746980 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The use of Open Dialogue in Trauma Informed Care services for mental health consumers and their family networks: A scoping review.J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2024 Aug;31(4):681-698. doi: 10.1111/jpm.13023. Epub 2024 Jan 17. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38230967
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
-
NIH Consensus Statement on Management of Hepatitis C: 2002.NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002 Jun 10-12;19(3):1-46. NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002. PMID: 14768714
References
-
- Ago Y, Van C, Condro MC, Hrncir H, Diep AL, Rajbhandari AK, Fanselow MS, Hashimoto H, MacKenzie-Graham AJ, Waschek JA (2023) Overexpression of VIPR2 in mice results in microencephaly with paradoxical increased white matter volume. Exp Neurol 362:114339. 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114339 - PubMed
-
- Alhouayek M, Masquelier J, Muccioli GG (2018) Lysophosphatidylinositols, from Cell membrane constituents to GPR55 ligands. Trends Pharmacol Sci 39(6):586–604. 10.1016/j.tips.2018.02.011 - PubMed
-
- Aljohani H, Alrubaish FS, Alghamdi WM, Al-Harbi F (2024) Safety of linagliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Ther Innov Regul Sci 58:622–633. 10.1007/s43441-024-00637-2 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

