The Progress of Cognitive Dysfunction Impairment Caused by Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
- PMID: 40542997
- PMCID: PMC12182514
- DOI: 10.1007/s12031-025-02365-0
The Progress of Cognitive Dysfunction Impairment Caused by Temporal Lobe Epilepsy
Abstract
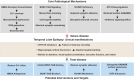
Epilepsy is a chronic disease that is characterized primarily by seizures. One of the most common and detrimental comorbidities of epilepsy is cognitive impairment. Approximately, 30-40% of patients with chronic epilepsy experience cognitive impairment, which significantly impacts their daily functioning and quality of life and imposes a heavy burden on both patients and society. Numerous studies have established a correlation between epilepsy and cognitive impairment, showing that epilepsy patients exhibit varying degrees of cognitive deficits influenced by various factors. However, the clinical manifestations, underlying mechanisms, and influencing factors of cognitive impairment in epilepsy patients are still not fully understood. In this review, we aim to summarize and integrate the current understanding of the mechanisms underlying learning and memory impairments in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE). We summarize the effects of abnormal neuronal discharges, synaptic plasticity alterations, neuroinflammation, and other potential contributors to cognitive dysfunction in TLE.
Keywords: ATF4; BDNF; Cognitive dysfunction; NCAM1; NMDA; Temporal lobe epilepsy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. During the preparation of this work, the author used LibreChat in order to improve language and readability. After using this tool/service, the author(s) reviewed and edited the content as needed and take(s) full responsibility for the content of the publication. Competing interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lamotrigine versus carbamazepine monotherapy for epilepsy: an individual participant data review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jun 28;6(6):CD001031. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001031.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29952431 Free PMC article.
-
Reading in children with temporal lobe epilepsy: A systematic review.Epilepsy Behav. 2017 Mar;68:84-94. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.12.021. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Epilepsy Behav. 2017. PMID: 28131931
-
Carbamazepine versus phenytoin monotherapy for epilepsy: an individual participant data review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Feb 27;2(2):CD001911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001911.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jul 18;7:CD001911. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001911.pub4. PMID: 28240353 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antiepileptic drug monotherapy for epilepsy: a network meta-analysis of individual participant data.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jun 29;6(6):CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 15;12:CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub3. PMID: 28661008 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Antiepileptic drug monotherapy for epilepsy: a network meta-analysis of individual participant data.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 15;12(12):CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Apr 1;4:CD011412. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011412.pub4. PMID: 29243813 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
-
- Abarrategui B, Parejo-Carbonell B, Garcia Garcia ME, Di Capua D, Garcia-Morales I (2018) The cognitive phenotype of idiopathic generalized epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 89:99–104 - PubMed
-
- Ali I, Boets S, Janssens P, Van Eetveldt A, Amhaoul H, Langlois X, Dedeurwaerdere S (2016) Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 density and its relation to the hippocampal neuropathology in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy in rats. Epilepsy Res 127:55–59 - PubMed
-
- Ameri K, Harris AL (2008) Activating transcription factor 4. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40(1):14–21 - PubMed
-
- Auvin S (2022) Paediatric epilepsy and cognition. Dev Med Child Neurol 64(12):1444–1452 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous