Esophageal and Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: Clinical Recommendations From the United European Gastroenterology and European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility
- PMID: 40543044
- PMCID: PMC12269739
- DOI: 10.1002/ueg2.70062
Esophageal and Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: Clinical Recommendations From the United European Gastroenterology and European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Esophageal and Oropharyngeal Dysphagia: Clinical Recommendations From the United European Gastroenterology and European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility".United European Gastroenterol J. 2025 Oct;13(8):1607. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.70088. Epub 2025 Jul 31. United European Gastroenterol J. 2025. PMID: 40746046 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
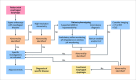
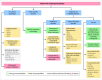
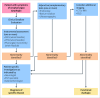
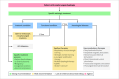
Dysphagia is a prevalent symptom of the upper gastrointestinal tract causing health related consequences, impacting quality of life and is associated with global economic burden. Swallowing difficulties are classified into oropharyngeal dysphagia (OD) and esophageal dysphagia. Despite its clinical importance, dysphagia is associated with several uncertainties regarding its optimal diagnostic work-up and management, particularly, considering the progress with diagnostic modalities and technologies. A Delphi consensus was performed with experts from various disciplines who conducted a literature summary and voting process on 41 statements. Quality of evidence was evaluated using the grading of recommendations, assessment, development, and evaluation criteria. Consensus was reached for all the statements. The panel agreed with the definition and prevalence of esophageal and OD types. The role of endoscopy, high-resolution manometry, EndoFLIP, barium swallow and other imaging tests in evaluating esophageal dysphagia has reached overall strong agreement. Videofluoroscopic swallow study, alongside fiber-endoscopic evaluation of swallowing, as the methods of choice for the instrumental assessment of oropharyngeal dysfunction is a strong recommendation. Regarding treatment, a weak recommendation was achieved for the use of PPIs, calcium-channel blockers, nitrates, phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors, antidepressants or peppermint oil for the treatment of hypercontractile esophagus. A strong recommendation exists for endoscopic and surgical treatment of achalasia, while a weak recommendation is provided for other esophageal motility disorders. Regarding OD, a weak recommendation was achieved for swallow therapy, to improve swallowing mechanics, reduce symptoms, and enhance quality of life. Swallow therapy could be more effective when using validated assessment tools, consistent treatment parameters, and considering long-term follow-up. A multinational group of European experts summarized the current state of consensus on the definition, diagnosis, and management of dysphagia.
Keywords: Delphi consensus; barium swallow; diagnosis; dysphagia; esophageal motility disorders; high resolution manometry (HRM); management; oropharyngeal dysphagia; workup.
© 2025 The Author(s). United European Gastroenterology Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of United European Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Amir Mari, Francesco Calabrese, Greta Lorenzon, Bas Weusten, Jutta Keller, Pierfrancesco Visaggi, Ram Dickman, Jordi Serra, Nicola De Bortoli, Paola Iovino, Dan Dumitrascu, Mentore Ribolsi, Claudia Barber, Serhat Bor, Mark Fox, Rami Sweiss, Vicente Lorenzo‐Zuniga, Filiz Akyuz, Matteo Ghisa, Altay Celebi, Fahmi Shibli, Rainer Dziewas, Ismail Hakkı Kalkan, Jan Tack, Pere Clavé, Silvia Carrion, Ivy Cheng, Noemi Tomsen, Omar Ortega, Sergio Marin Rubio, Nicole Pizzorni, Emilia Michou, Julie Regan, Nathalie Rommel, Martina Scharitzer, Olle Ekberg, Antonio Schindler, Renee Speyer, and Anna Gillman: no conflict of interest to declare; Andrea Pasta: Consultant for FenixPharma; Sabine Roman: Consultant for Dr Falk Pharma, Sanofi; Research support from Medtronic, Diversatek Healthcare; Elisa Marabotto: Consultant AlphaSigma, Dr. Falk; Daniel Pohl: Consultant and Speaker Medtronic; Shaheen Hamdy: Chief Scientific Officer of Phagenesis Ltd, and holds stocks/shares in that company; Frank Zerbib: Consultant for Medtronic, Dr Falk Pharma, Bioprojet, Sanofi, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb; Edoardo V. Savarino: Speaker for Abbvie, Abivax, Agave, AGPharma, Alfasigma, Apoteca, Biosline, CaDiGroup, Celltrion, Dr Falk, EG Stada Group, Fenix Pharma, Galapagos, Johnson & Johnson, JB Pharmaceuticals, Innovamedica/Adacyte, Eli Lilly, Malesci, Mayoly Biohealth, Montefarco, Novartis, Omega Pharma, Pfizer, Rafa, Reckitt Benckiser, Sandoz, Sanofi/Regeneron, SILA, Sofar, Takeda, Tillots, Unifarco; has served as consultant for Abbvie, Agave, Alfasigma, Biogen, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Celltrion, Dr. Falk, Eli Lilly, Fenix Pharma, Ferring, Giuliani, Grunenthal, Johnson & Johnson, JB Pharmaceuticals, Merck & Co, Nestlè, Pfizer, Reckitt Benckiser, Sanofi/Regeneron, SILA, Sofar, Takeda, Unifarco; he received research support from Bonollo, Difass, Pfizer, Reckitt Benckiser, Sanofi/Regeneron, SILA, Sofar, Unifarco, Zeta Farmaceutici.
Figures