Exploring Telitacicept for Neurological Autoimmune Disorders: A Case Study on Morvan Syndrome
- PMID: 40543057
- PMCID: PMC12188942
- DOI: 10.12659/AJCR.947004
Exploring Telitacicept for Neurological Autoimmune Disorders: A Case Study on Morvan Syndrome
Abstract
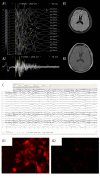
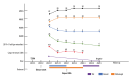
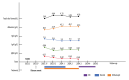
BACKGROUND Morvan syndrome is an autoimmune disease associated with autoantibodies against proteins of the voltage-gated potassium channel complex, particularly Caspr2. Telitacicept, a recombinant TACI-Fc fusion protein that dually inhibits BAFF and APRIL cytokines, has shown efficacy in refractory autoimmune diseases. This report describes a 54-year-old man with Morvan syndrome presenting with peripheral nerve hyperexcitability and sleep disturbance who responded to telitacicept after conventional immunotherapy failed. CASE REPORT In September 2023, a 54-year-old male patient presented with weakness, muscle cramps, burning sensation, pain in both lower limbs, and walking instability. He also reported severe sleep disturbance, cognitive impairment, difficulty concentrating, restlessness, and depression. Physical examination revealed muscle fasciculation, myokymia, hyperhidrosis, frequent micturition, and significant weight loss. Laboratory test results confirmed positive anti-Caspr2 antibodies in the serum. Due to pre-existing blood glucose concerns, the patient declined high-dose corticosteroid pulse therapy. After thorough discussion of alternative options, including intravenous immunoglobulin, plasma exchange, and rituximab, the patient opted for subcutaneous telitacicept at a dose of 160 mg weekly. Within the second week of treatment, notable improvements were observed in muscle myokymia, neuropathic pain, and sleep disturbances. Over the following 6 months, the patient achieved complete clinical remission with no recurrence of symptoms and was able to discontinue corticosteroids. No infections or other adverse effects were reported during the treatment period. CONCLUSIONS This report has highlighted the approach to diagnosing Morvan syndrome, which can present with peripheral nerve hyperexcitability, and supports the role of immunomodulatory therapy, including telitacicept.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Corticosteroids for the treatment of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 5;2016(5):CD003725. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003725.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27149418 Free PMC article.
-
Unmasking Anti-CASPR2 Syndrome in a Patient Treated for Myasthenia Gravis in the Era of New Treatments.Eur J Neurol. 2025 Jul;32(7):e70285. doi: 10.1111/ene.70285. Eur J Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40631640 Free PMC article.
-
Treatments for chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP): an overview of systematic reviews.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jan 13;1(1):CD010369. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010369.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28084646 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
-
Methotrexate for induction of remission in refractory Crohn's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Dec 12;12:CD003459. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003459.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Aug 06;(8):CD003459. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003459.pub4. PMID: 23235598 Updated.
References
-
- Liguori R, Vincent A, Clover L, et al. Morvan’s syndrome: Peripheral and central nervous system and cardiac involvement with antibodies to voltage-gated potassium channels. Brain. 2001;124:2417–26. - PubMed
-
- Masood W, Lui F, Sitammagari KK. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): ineligible companies; 2025. Morvan syndrome. Disclosure: Forshing Lui declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. Disclosure: Kranthi Sitammagari declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies. - PubMed
-
- van Sonderen A, Petit-Pedrol M, Dalmau J, Titulaer MJ. The value of LGI1, Caspr2 and voltage-gated potassium channel antibodies in encephalitis. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13:290–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

