High dietary astaxanthin supplementation alters egg yolk nutritional composition in hens
- PMID: 40543259
- PMCID: PMC12221448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105393
High dietary astaxanthin supplementation alters egg yolk nutritional composition in hens
Abstract
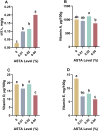
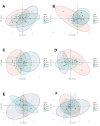
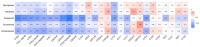
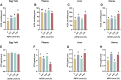
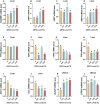
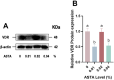
Astaxanthin (ASTA), a potent antioxidant with anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative, and anti-apoptotic effects, has garnered attention for its potential to enhance the nutritional value of eggs. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of dietary ASTA on egg yolk nutritional composition, sensory attributes, and related molecular mechanisms. We assessed how varying levels of ASTA supplementation (0, 0.01 %, 0.02 %, and 0.04 %) influenced yolk color, texture, and nutrient profile. The results showed that dietary ASTA had no significant effect on laying productive performance but enhanced yolk color in a dose-dependent manner (P < 0.05). Texture analysis showed that ASTA reduced the cohesiveness and chewiness of yolks (P < 0.05), while electronic tongue analysis confirmed no significant impact on flavor. ASTA did not significantly alter amino acid composition but increased total fatty acid content in the 0.02 % and 0.04 % groups (P < 0.05). Compared with the control group, the content of vitamin E in egg yolk significantly (P < 0.05) decreased in the ASTA groups, and the contents of vitamin D in egg yolk significantly (P < 0.05) decreased in the 0.01 % and 0.04 % ASTA groups, which corresponded with inhibited expression of alpha-tocopherol transfer protein (TTPA) and vitamin D receptor (VDR) mRNA, as well as reduced VDR protein levels. ASTA further upregulated the expression of nutrient-transport proteins, including very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) (P < 0.05), demonstrating its role in modulating nutrient transport and distribution. This research underscores the importance of balancing ASTA levels to optimize both nutrient enhancement and preservation of existing beneficial compounds in fortified eggs. Our research findings provide valuable insights for the production of ASTA-enriched eggs, enabling consumers to select nutritionally fortified eggs according to their own nutritional needs.
Keywords: Astaxanthin; Astaxanthin-fortified egg; Fatty acids; Vitamin D; Vitamin E.
Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bourre J.M., Galea F. An important source of omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins D and E, carotenoids, iodine and selenium: a new natural multi-enriched egg. J. Nutr. Health Aging. 2006;10(5):371–376. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

