Chiral phosphoric acid-catalyzed atroposelective iodination of N-arylindoles
- PMID: 40544218
- PMCID: PMC12182571
- DOI: 10.1038/s42004-025-01584-1
Chiral phosphoric acid-catalyzed atroposelective iodination of N-arylindoles
Abstract
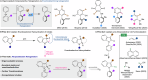
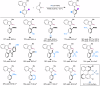
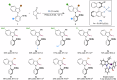
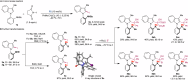
Axially chiral indoles have garnered significant attention due to their synthetic and biological importance. However, atroposelective halogenation of this scaffold has been rarely explored. This study presents a catalytic and enantioselective iodination of N-arylindoles, achieving precise control over the C-N stereogenic axis. The reaction is facilitated by a chiral phosphoric acid, which promotes iodination at the C-3 position of N-arylindole, followed by iodine migration and deprotonation. A hydrogen-bonding donor on the aromatic ring plays a key role in achieving high enantioselectivities. Under optimized reaction conditions, a wide range of substrates are well-tolerated, and subsequent reactions with various carbonyl electrophiles maintain enantioselectivity. Computational studies provide insights into the origin of enantioselectivity at the plausible enantiodetermining step.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Liu, Y., Leng, H.-J., Li, Q.-Z. & Li, J.-L. Catalytic strategies for the asymmetric construction of cyclic frameworks with a halogenated tetrasubstituted stereocenter. Adv. Synth. Catal.362, 3926–3947 (2020).
-
- Wong, J. & Yeung, Y.-Y. Recent advances in C–Br bond formation. Synlett32, 1354–1364 (2021).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

